Learning Pose Grammar to Encode Human Body Configuration for 3D Pose
Estimation
Learning Pose Grammar to Encode Human Body Configuration for 3D Pose Estimation
Fang Haoshu Xu Yuanlu Wang Wenguan Liu Xiaobai Zhu Song-Chun
Abstract
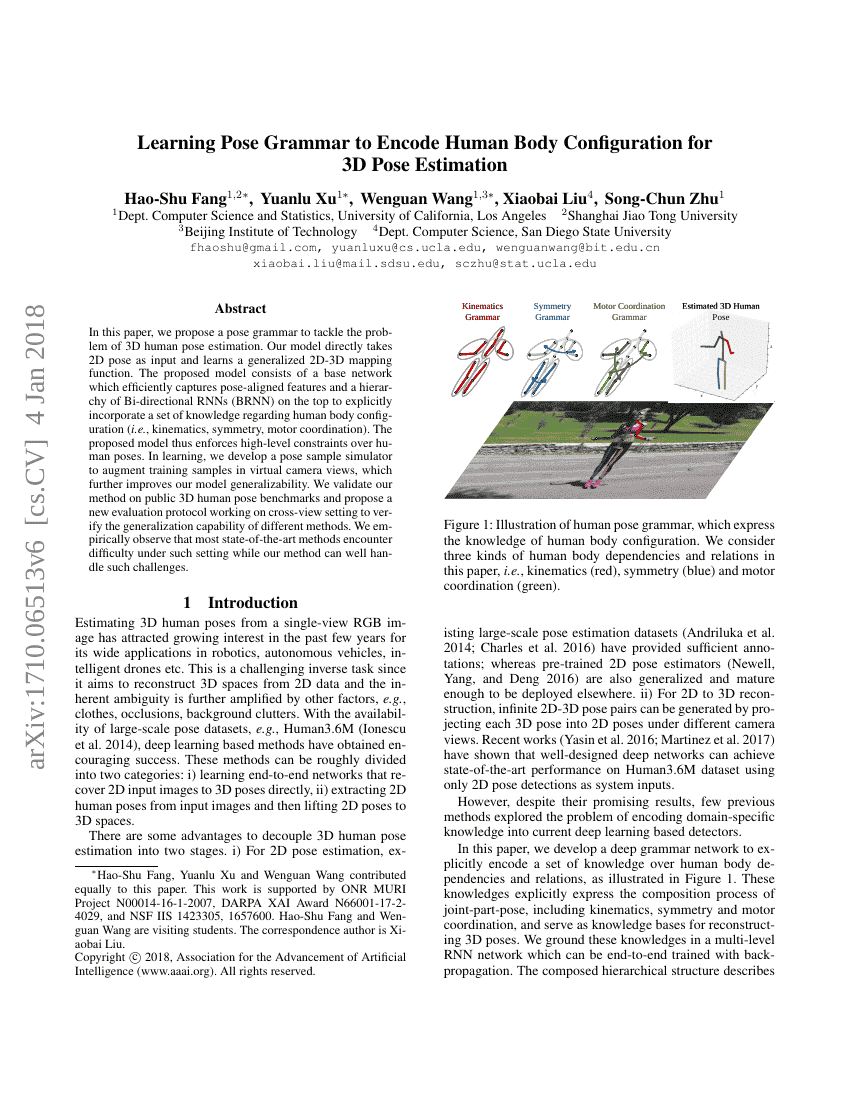
In this paper, we propose a pose grammar to tackle the problem of 3D humanpose estimation. Our model directly takes 2D pose as input and learns ageneralized 2D-3D mapping function. The proposed model consists of a basenetwork which efficiently captures pose-aligned features and a hierarchy ofBi-directional RNNs (BRNN) on the top to explicitly incorporate a set ofknowledge regarding human body configuration (i.e., kinematics, symmetry, motorcoordination). The proposed model thus enforces high-level constraints overhuman poses. In learning, we develop a pose sample simulator to augmenttraining samples in virtual camera views, which further improves our modelgeneralizability. We validate our method on public 3D human pose benchmarks andpropose a new evaluation protocol working on cross-view setting to verify thegeneralization capability of different methods. We empirically observe thatmost state-of-the-art methods encounter difficulty under such setting while ourmethod can well handle such challenges.
Benchmarks
| Benchmark | Methodology | Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| 3d-absolute-human-pose-estimation-on-human36m | Pose Grammar | Average MPJPE (mm): 60.4 |
| 3d-human-pose-estimation-on-human36m | Pose Grammar | Average MPJPE (mm): 60.4 PA-MPJPE: 45.7 |
| 3d-human-pose-estimation-on-humaneva-i | Pose Grammar | Mean Reconstruction Error (mm): 22.9 |
Build AI with AI
From idea to launch — accelerate your AI development with free AI co-coding, out-of-the-box environment and best price of GPUs.