Representation Learning for Heterogeneous Information Networks via Embedding Events
Representation Learning for Heterogeneous Information Networks via Embedding Events
Guoji Fu Qiqi Duan Bo Yuan Xin Yao
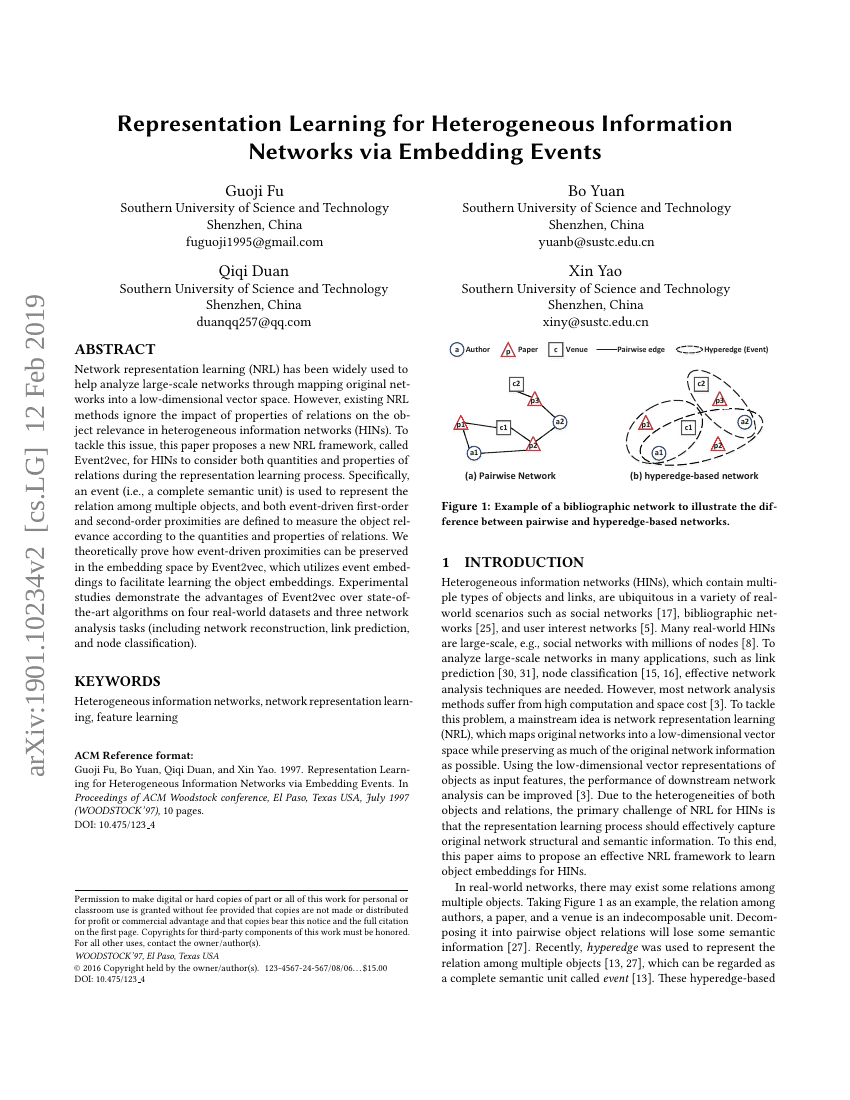
Abstract
Network representation learning (NRL) has been widely used to help analyze large-scale networks through mapping original networks into a low-dimensional vector space. However, existing NRL methods ignore the impact of properties of relations on the object relevance in heterogeneous information networks (HINs). To tackle this issue, this paper proposes a new NRL framework, called Event2vec, for HINs to consider both quantities and properties of relations during the representation learning process. Specifically, an event (i.e., a complete semantic unit) is used to represent the relation among multiple objects, and both event-driven first-order and second-order proximities are defined to measure the object relevance according to the quantities and properties of relations. We theoretically prove how event-driven proximities can be preserved in the embedding space by Event2vec, which utilizes event embeddings to facilitate learning the object embeddings. Experimental studies demonstrate the advantages of Event2vec over state-of-the-art algorithms on four real-world datasets and three network analysis tasks (including network reconstruction, link prediction, and node classification).
Code Repositories
Benchmarks
| Benchmark | Methodology | Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| link-prediction-on-dblp | Event2vec | AUC: 90.1 |
| link-prediction-on-douban | Event2vec | AUC: 82.3 |
| link-prediction-on-imdb | Event2vec | AUC: 89.4 |
| link-prediction-on-yelp | Event2vec | AUC: 86.2 |
Build AI with AI
From idea to launch — accelerate your AI development with free AI co-coding, out-of-the-box environment and best price of GPUs.