Improving Pedestrian Attribute Recognition With Weakly-Supervised Multi-Scale Attribute-Specific Localization
Improving Pedestrian Attribute Recognition With Weakly-Supervised Multi-Scale Attribute-Specific Localization
Chufeng Tang Lu Sheng Zhaoxiang Zhang Xiaolin Hu
Abstract
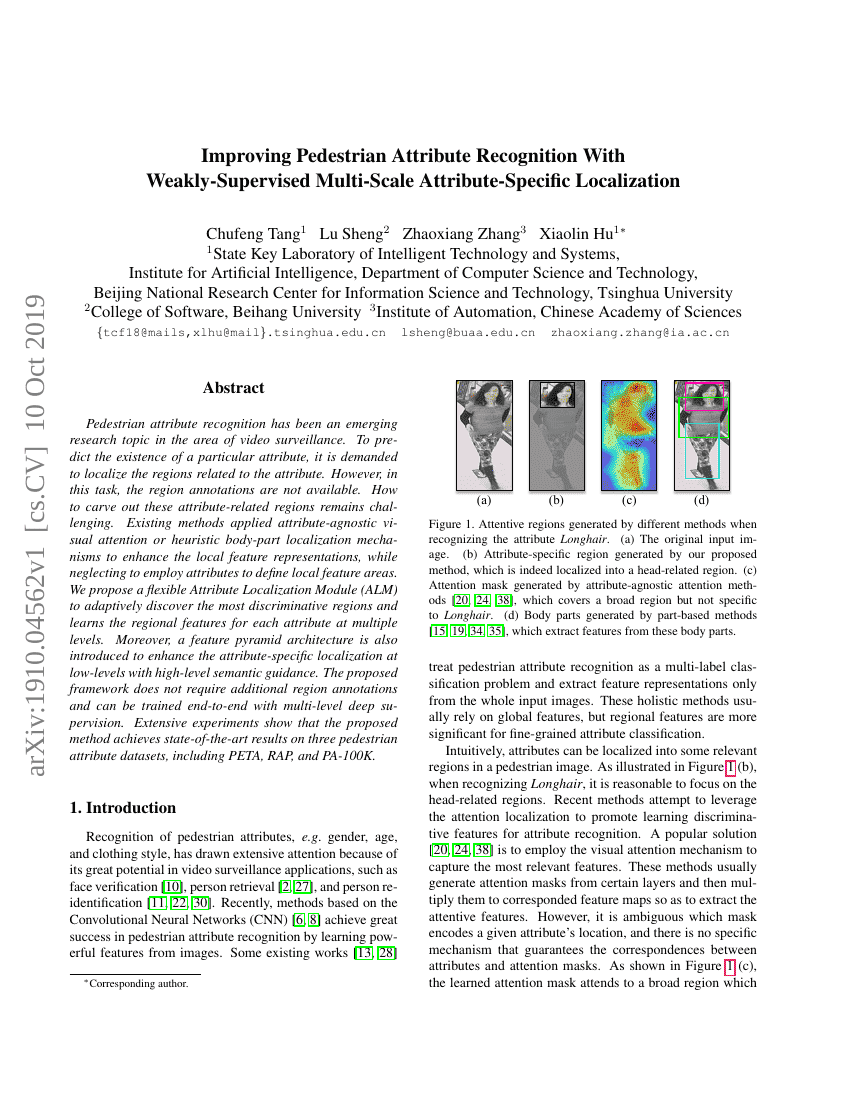
Pedestrian attribute recognition has been an emerging research topic in the area of video surveillance. To predict the existence of a particular attribute, it is demanded to localize the regions related to the attribute. However, in this task, the region annotations are not available. How to carve out these attribute-related regions remains challenging. Existing methods applied attribute-agnostic visual attention or heuristic body-part localization mechanisms to enhance the local feature representations, while neglecting to employ attributes to define local feature areas. We propose a flexible Attribute Localization Module (ALM) to adaptively discover the most discriminative regions and learns the regional features for each attribute at multiple levels. Moreover, a feature pyramid architecture is also introduced to enhance the attribute-specific localization at low-levels with high-level semantic guidance. The proposed framework does not require additional region annotations and can be trained end-to-end with multi-level deep supervision. Extensive experiments show that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art results on three pedestrian attribute datasets, including PETA, RAP, and PA-100K.
Code Repositories
Benchmarks
| Benchmark | Methodology | Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| pedestrian-attribute-recognition-on-pa-100k | Attribute-Specific Localization | Accuracy: 77.08% |
| pedestrian-attribute-recognition-on-peta | Attribute-Specific Localization | Accuracy: 79.52% |
| pedestrian-attribute-recognition-on-rap | Attribute-Specific Localization | Accuracy: 68.17% |
Build AI with AI
From idea to launch — accelerate your AI development with free AI co-coding, out-of-the-box environment and best price of GPUs.