The Consistency Critic: Correcting Inconsistencies in Generated Images via Reference-Guided Attentive Alignment
The Consistency Critic: Correcting Inconsistencies in Generated Images via Reference-Guided Attentive Alignment
Ziheng Ouyang Yiren Song Yaoli Liu Shihao Zhu Qibin Hou Ming-Ming Cheng Mike Zheng Shou

Abstract
Previous works have explored various customized generation tasks given a reference image, but they still face limitations in generating consistent fine-grained details. In this paper, our aim is to solve the inconsistency problem of generated images by applying a reference-guided post-editing approach and present our ImageCritic. We first construct a dataset of reference-degraded-target triplets obtained via VLM-based selection and explicit degradation, which effectively simulates the common inaccuracies or inconsistencies observed in existing generation models. Furthermore, building on a thorough examination of the model's attention mechanisms and intrinsic representations, we accordingly devise an attention alignment loss and a detail encoder to precisely rectify inconsistencies. ImageCritic can be integrated into an agent framework to automatically detect inconsistencies and correct them with multi-round and local editing in complex scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ImageCritic can effectively resolve detail-related issues in various customized generation scenarios, providing significant improvements over existing methods.
Summarization
Researchers from Nankai University, National University of Singapore, and Zhejiang University introduce ImageCritic, a reference-guided post-editing framework that employs a novel attention alignment loss and detail encoder to automatically detect and rectify fine-grained inconsistencies in generated images within complex customized scenarios.
Introduction
Recent advancements in image generation have shifted from UNet architectures to Transformer-based Diffusion models (DiTs), driving progress in reference-guided applications such as virtual try-on, image editing, and subject customization. While these systems aim to integrate specific subjects into new contexts, achieving precise consistency between the generated output and the reference image remains a critical challenge for high-fidelity real-world deployment.
Current state-of-the-art models frequently suffer from inconsistent or blurry fine-grained details, such as text, logos, and complex textures, largely due to information loss inherent in VAE-based encoding and decoder-only structures. Standard solutions like super-resolution or multi-image editing often fail to accurately localize these specific discrepancies or correct structural errors. Additionally, the field lacks high-quality datasets focused on subtle local details, as existing benchmarks prioritize overall object consistency over minute structural alignment.
To address these issues, the authors introduce ImageCritic, a unified post-editing correction framework designed to detect and repair local inconsistencies in customized generation.
Key Innovations
- Reference-Degraded-Target Dataset: The researchers constructed a specialized dataset using VLM-based selection and explicit degradation to simulate real-world generation errors, creating a benchmark that focuses specifically on recovering fine-grained details rather than just general semantic consistency.
- Precision Alignment Mechanisms: The model utilizes an attention alignment loss to effectively decouple and localize regions requiring correction, paired with a detail encoder that explicitly embeds features from both reference and input images to improve generalization and structural fidelity.
- Agent-Based Processing Chain: The authors designed an automated agent system that manages the entire workflow, including consistency evaluation, discrepancy localization, and image refinement, enabling both one-click automated fixing and multi-round human-agent interaction.
Dataset
The authors construct a specialized dataset designed to address fine-grained consistency and detail misalignment in generated images. The data curation pipeline involves the following steps:
- Data Collection and Generation: The process begins with a large-scale collection of web-crawled product images. To expand diversity, the authors generate synthetic variants using state-of-the-art text-to-image models such as Flux Kontext, GPT-4o, and Nano-Banana, creating scene-rich images with varied objects and lighting conditions.
- VLM-Based Filtering and Annotation: Qwen-VL and Qwen3-vl are employed to filter samples based on visual clarity and text readability. The authors also use Qwen to assign semantic tags for object categorization and to perform image grounding, which identifies bounding boxes for specific objects within the generated scenes.
- Segmentation and Verification: Using the predicted bounding boxes, Grounding SAM extracts precise object masks. To ensure accuracy, Qwen re-evaluates these masks against the reference products, verifying that the extracted regions match the reference in terms of shape, color, and texture while filtering out inconsistencies.
- Controlled Degradation: To simulate real-world artifacts, the authors use Flux-Fill to actively corrupt 20% to 70% of the verified object regions. This step introduces specific errors, such as distorted English or Chinese text and mismatched logos, while a final composition step blends these degraded regions with the original background to isolate the artifacts.
- Dataset Composition: The final dataset consists of 10,000 high-quality triplets, each containing a reference image, a degraded input, and a ground-truth target. This structure provides the model with realistic supervision signals for repairing text rendering errors and logo misalignments.
- Iterative Enhancement: The authors utilize an iterative strategy where the model's own restored outputs are cropped and assessed for consistency. These corrected images are fed back into the dataset as improved targets, progressively refining the data quality for subsequent training cycles.
Experiment
- Implementation utilizes Flux.1-Kontext-dev as the base model with LoRA fine-tuning, employing the proposed ImageCritic to enhance dataset generation targets for improved consistency.
- Qualitative comparisons against open-source and closed-source models (e.g., XVerse, GPT-Image) demonstrate the method's superior ability to correct fine-grained details while preserving original lighting, texture, and background fidelity.
- Quantitative evaluations on Dreambench++ and the newly introduced CriticBench (focusing on complex details like text and logos) show substantial improvements in CLIP, DINO, and DreamSim scores compared to baselines.
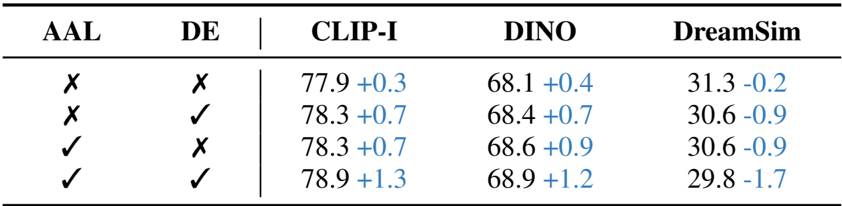
- Ablation studies confirm the individual and synergistic effectiveness of the proposed dataset, Attention Alignment Loss (AAL), and Detail Encoder (DE) in enhancing attention disentanglement and target region localization.
- The proposed agent chain exhibits strong localization performance, achieving a mean IoU of 75.3% and a mean mAP@50 of 88.4% against human-annotated ground truth.
- Additional visual and OCR-based assessments verify the method's robustness across diverse languages, viewpoints, and stylization settings.
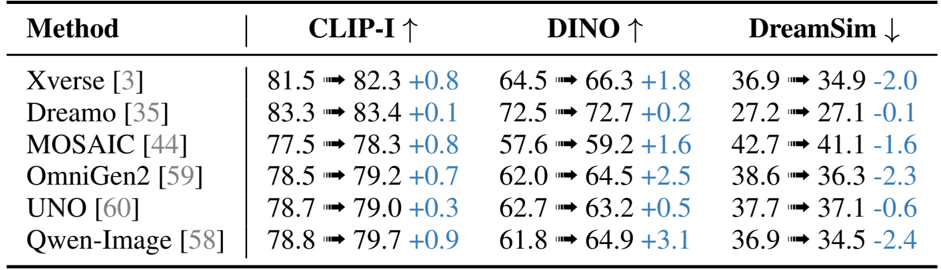
Results show that the proposed method achieves significant improvements in image consistency across multiple benchmarks, outperforming existing models such as Xverse, DreamO, and Qwen-Image in CLIP-I and DINO scores while maintaining or improving DreamSim values. The enhancements are particularly evident in fine-grained detail preservation, where the method consistently corrects inconsistencies in texture, color, and text while preserving background fidelity.
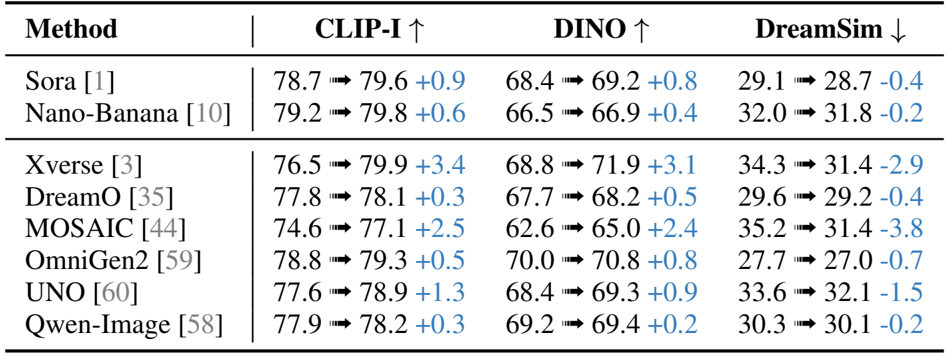
Results show that the proposed method improves consistency across multiple evaluation metrics, with significant gains in CLIP-I, DINO, and DreamSim scores compared to baseline models. The improvements indicate enhanced detail preservation and alignment with reference images, particularly in fine-grained visual elements.
Results show that combining Attention Alignment Loss (AAL) and Detail Encoder (DE) leads to the highest improvement in consistency metrics across CLIP-I, DINO, and DreamSim. The ablation study confirms that both components contribute independently to performance, with their combined use yielding the most significant gains.
The authors evaluate the performance of their agent chain in localizing fine-grained details by comparing automatically predicted bounding boxes with human annotations, using Intersection over Union (IoU) and mean Average Precision at 50% IoU (mAP@50). Results show a mean IoU of 75.3% and a mean mAP@50 of 88.4%, indicating strong alignment between the agent's predictions and ground truth, demonstrating its effectiveness in accurately identifying and correcting specific regions.

Build AI with AI
From idea to launch — accelerate your AI development with free AI co-coding, out-of-the-box environment and best price of GPUs.