Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
ArenaRL: Scaling RL for Open-Ended Agents via Tournament-based Relative Ranking
ArenaRL: Scaling RL for Open-Ended Agents via Tournament-based Relative Ranking
Abstract
Reinforcement learning has substantially improved the performance of LLM agents on tasks with verifiable outcomes, but it still struggles on open-ended agent tasks with vast solution spaces (e.g., complex travel planning). Due to the absence of objective ground-truth for these tasks, current RL algorithms largely rely on reward models that assign scalar scores to individual responses. We contend that such pointwise scoring suffers from an inherent discrimination collapse: the reward model struggles to distinguish subtle advantages among different trajectories, resulting in scores within a group being compressed into a narrow range. Consequently, the effective reward signal becomes dominated by noise from the reward model, leading to optimization stagnation. To address this, we propose ArenaRL, a reinforcement learning paradigm that shifts from pointwise scalar scoring to intra-group relative ranking. ArenaRL introduces a process-aware pairwise evaluation mechanism, employing multi-level rubrics to assign fine-grained relative scores to trajectories. Additionally, we construct an intra-group adversarial arena and devise a tournament-based ranking scheme to obtain stable advantage signals. Empirical results confirm that the built seeded single-elimination scheme achieves nearly equivalent advantage estimation accuracy to full pairwise comparisons with O(N^2) complexity, while operating with only O(N) complexity, striking an optimal balance between efficiency and precision. Furthermore, to address the lack of full-cycle benchmarks for open-ended agents, we build Open-Travel and Open-DeepResearch, two high-quality benchmarks featuring a comprehensive pipeline covering SFT, RL training, and multi-dimensional evaluation. Extensive experiments show that ArenaRL substantially outperforms standard RL baselines, enabling LLM agents to generate more robust solutions for complex real-world tasks.
One-sentence Summary
The authors from Tongyi Lab and Amap, Alibaba Group propose ArenaRL, a novel reinforcement learning framework that replaces pointwise scalar rewards with intra-group relative ranking via a process-aware pairwise evaluation and tournament-based scheme, achieving efficient O(N) advantage estimation while overcoming discrimination collapse in open-ended tasks like complex travel planning, and demonstrate superior performance on newly introduced Open-Travel and Open-DeepResearch benchmarks.
Key Contributions
-
Open-ended LLM agent tasks, such as complex travel planning, lack objective ground-truth rewards, forcing current reinforcement learning methods to rely on pointwise scalar scoring from LLM judges, which suffers from discriminative collapse—where similar trajectories receive nearly identical scores, obscuring meaningful performance differences due to high reward noise.
-
ArenaRL addresses this by introducing a novel paradigm shift from pointwise scoring to intra-group relative ranking, using a process-aware pairwise evaluation with multi-level rubrics and a tournament-based ranking scheme that achieves near-optimal accuracy with only O(N) complexity, significantly improving efficiency over O(N²) full pairwise comparisons.
-
The framework is validated on new benchmarks—Open-Travel and Open-DeepResearch—featuring full-cycle training and multi-dimensional evaluation, demonstrating that ArenaRL enables more logically rigorous and robust agent behavior, substantially outperforming standard RL baselines like GRPO and GSPO.
Introduction
Reinforcement learning (RL) has advanced large language model (LLM) agents in tasks with verifiable outcomes like math and code, but struggles with open-ended real-world problems such as travel planning or deep research, where solution spaces are vast and correctness is subjective. Prior methods rely on LLM-as-Judge to assign pointwise scalar rewards, but this leads to discriminative collapse—where high-quality trajectories receive nearly identical scores due to reward model noise and limited discriminability—resulting in ineffective optimization. To overcome this, the authors propose ArenaRL, a tournament-based RL framework that replaces pointwise scoring with intra-group relative ranking. ArenaRL uses a process-aware pairwise evaluation with multi-level rubrics to assess reasoning, tool use, and outcomes, and introduces a seeded single-elimination tournament that achieves near-optimal ranking accuracy with only O(N) complexity, enabling efficient and stable advantage estimation. The authors further introduce Open-Travel and Open-DeepResearch, full-cycle benchmarks with integrated SFT, RL training, and multi-dimensional evaluation pipelines, enabling reproducible study of open-ended agents. Experiments show ArenaRL significantly outperforms baselines in logical rigor and robustness across complex, real-world tasks.
Dataset
- The dataset comprises two domains: Open-Travel and Open-DeepResearch, constructed through a three-stage pipeline to simulate real-world business scenarios.
- Open-Travel includes five subtasks: Direction (multi-waypoint route planning), 1-Day (one-day city trip), Compare (transportation mode comparison), Search (nearby POI discovery), and M-Day (multi-day trip planning), with the latter excluded from SFT training.
- Open-DeepResearch focuses on open-ended research tasks such as technical document writing, research ideation, and concept summarization, requiring multi-turn tool use and synthesis.
- Training data is built from real business queries and LLM-generated expansions using diverse models (e.g., Qwen3, Qwen3-Max), resulting in 2,600 SFT samples for Open-Travel and 2,662 for Open-DeepResearch, plus 1,626 and 2,216 RL samples respectively.
- Test sets consist of 250 manually curated Open-Travel samples and 100 Open-DeepResearch samples, selected for clarity, diversity, and difficulty, and verified by domain experts.
- Baseline trajectories for evaluation are generated using high-performing closed-source models to establish a reference for win-rate comparisons.
- All trajectories undergo LLM-based quality control with rule-augmented inspection, assessing tool usage effectiveness, conversational correctness, and answer consistency, with failed cases iteratively refined.
- For Open-Travel, six tools are annotated: search_poi, around_search, get_navigation, universal_search, search_flights, and search_train_tickets, implemented via Amap APIs and simulated flight/train data.
- For Open-DeepResearch, web search is conducted via Google API, with content exceeding 2,500 characters automatically summarized using Qwen3-Max to manage context length.
- The authors use the SFT data to train the model on tool calling, intent understanding, and multi-step reasoning, while RL samples are used to optimize open-ended agentic behavior under realistic constraints.
- The dataset spans diverse domains beyond travel, including sports, medicine, and professional scenarios, enabling evaluation of general-purpose agent capabilities.
Method
The authors leverage a novel reinforcement learning framework, ArenaRL, to address the instability of pointwise scalar rewards in open-ended agent tasks. The core of the method revolves around replacing conventional scalar reward signals with a relative ranking mechanism that evaluates trajectories within a group. This approach is designed to mitigate discriminative collapse by focusing on intra-group comparisons rather than absolute quality scores. The overall framework, as illustrated in the figure below, consists of two main stages: a cold start phase where the agent generates trajectories through interaction with the environment, and an ArenaRL-based online relative ranking optimization phase that iteratively refines the policy.
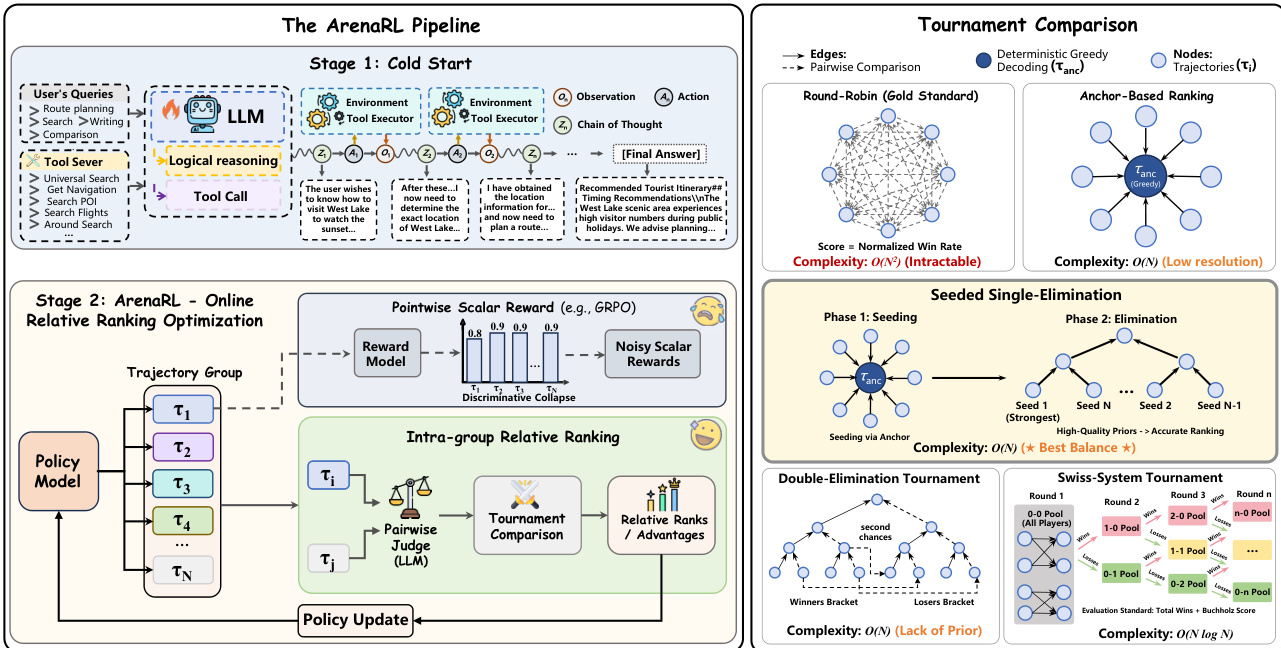
In ArenaRL, the process begins by sampling a group of trajectories G={τ1,τ2,…,τN} from the current policy πθ. The quality of these trajectories is assessed using a process-aware pairwise evaluation mechanism, which is implemented by an LLM-based Arena Judge. This judge evaluates two trajectories, τi and τj, jointly against a comprehensive rubric that scrutinizes the logical consistency of the chain-of-thought, the precision of tool calls, and the reliability of the final answer. To mitigate positional bias, a bidirectional scoring protocol is employed, where the trajectories are evaluated in both possible orders and the scores are summed.
The framework systematically investigates five distinct tournament topologies to balance computational efficiency with the accuracy of advantage estimation. The Round-Robin tournament, which compares every trajectory against all others, serves as a gold standard for ranking fidelity but is computationally intractable with O(N2) complexity. To achieve linear complexity O(N), the Anchor-Based Ranking mechanism is introduced, where a deterministic reference trajectory (the anchor) is compared against all other exploratory trajectories. However, this method suffers from a loss of resolution in ranking among suboptimal solutions. To bridge this trade-off, the authors propose the Seeded Single-Elimination tournament, a hybrid topology that operates in two phases. The first phase uses the anchor-based ranking to generate a high-quality initial seeding, which is critical for preventing high-quality trajectories from colliding prematurely. The second phase constructs a binary tournament tree based on these seeds, where match-ups are arranged to ensure a fair competition. The final ranking is determined by the depth of survival within the bracket, with intra-tier ties resolved using accumulated average scores from previous matches.
The Seeded Single-Elimination topology is highlighted as the optimal choice, achieving a best balance between accuracy and efficiency. The ranking of each trajectory is converted into a normalized advantage signal for policy optimization. This process involves mapping the discrete rank to a quantile-based reward, standardizing the rewards within the group, and then using a clipped objective function to update the policy. The final optimization objective incorporates a KL-divergence penalty to prevent excessive deviation from a reference policy, ensuring stable and effective policy updates. The detailed procedure for the Seeded Single-Elimination tournament is outlined in Algorithm 1, which formalizes the seeding, elimination, ranking, and advantage calculation steps.
Experiment
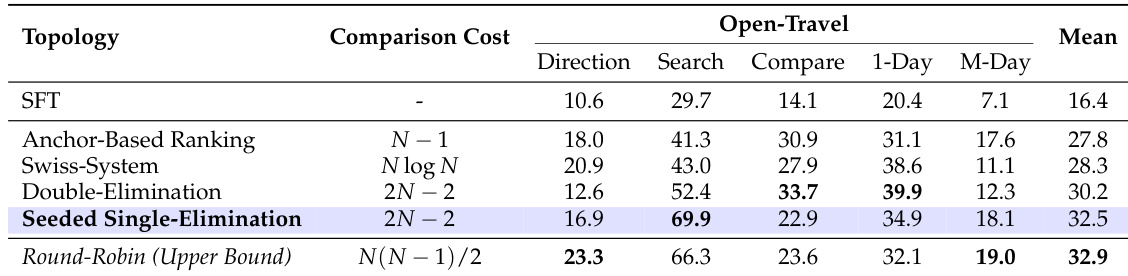
- Evaluated five tournament topologies (Seeded Single-Elimination, Round-Robin, Swiss-System, Double-Elimination, and others) on Open-Travel, showing Seeded Single-Elimination achieves 32.5% average win rate—comparable to Round-Robin (32.9%) but with O(N) complexity, validating its efficiency and effectiveness.
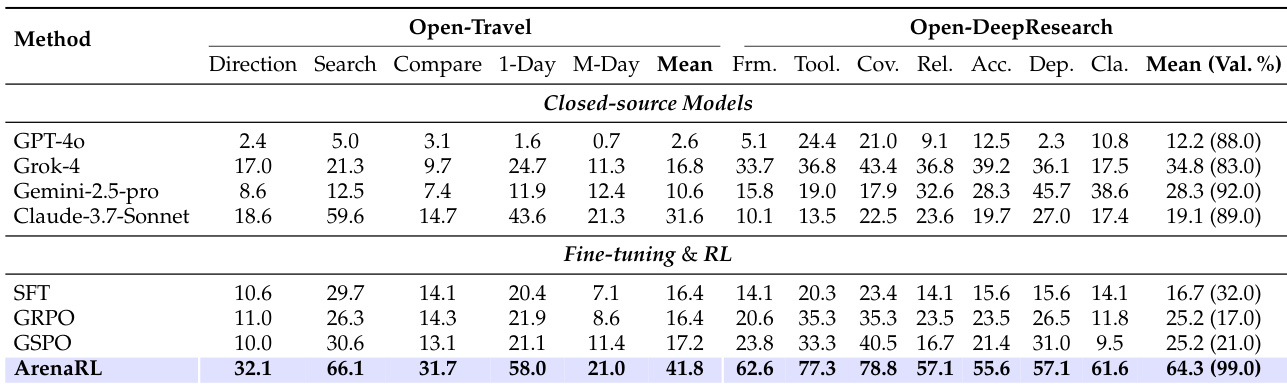
- On Open-Travel, ArenaRL achieves 41.8% average win rate, surpassing GPT-4o, Grok-4, Gemini-2.5-pro, Claude-3.7-Sonnet, GRPO (16.4%), and GSPO (17.2%).
- On Open-DeepResearch, ArenaRL achieves 64.3% win rate and 99% valid generation rate, significantly outperforming baselines with only 32% valid generation for the SFT model, highlighting its robustness in long-horizon, context-sensitive tasks.
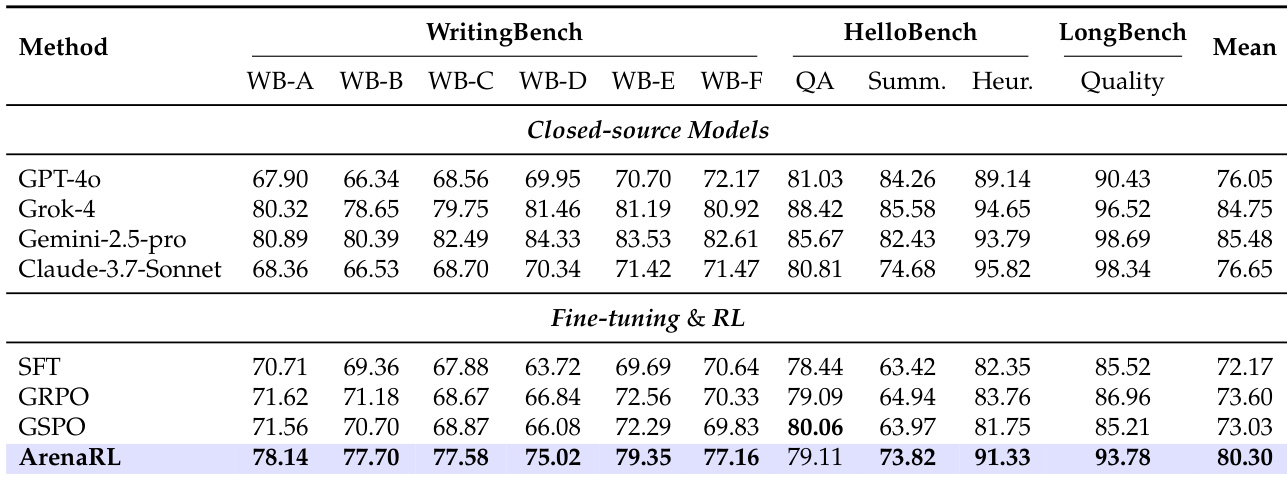
- On three public open-ended writing benchmarks (WritingBench, HelloBench, LongBench-write), ArenaRL outperforms GRPO by 6.70% and GSPO by 7.27%, and surpasses GPT-4o and Claude-3.7-Sonnet, demonstrating broad applicability beyond agent tasks.
- Real-world evaluation on Amap (Gaode Map) data shows ArenaRL improves search accuracy by 75–83% in deterministic POI tasks and boosts core business metrics from 69% to 80% in complex open-ended planning, confirming practical effectiveness.
- Ablation studies confirm that increasing group size (N) improves performance monotonically, with N=16 yielding 41.8% win rate on Open-Travel, and direct RL training without cold start shows stable, rapid improvement from 0% to 71% on Search subtask, proving self-evolution capability.
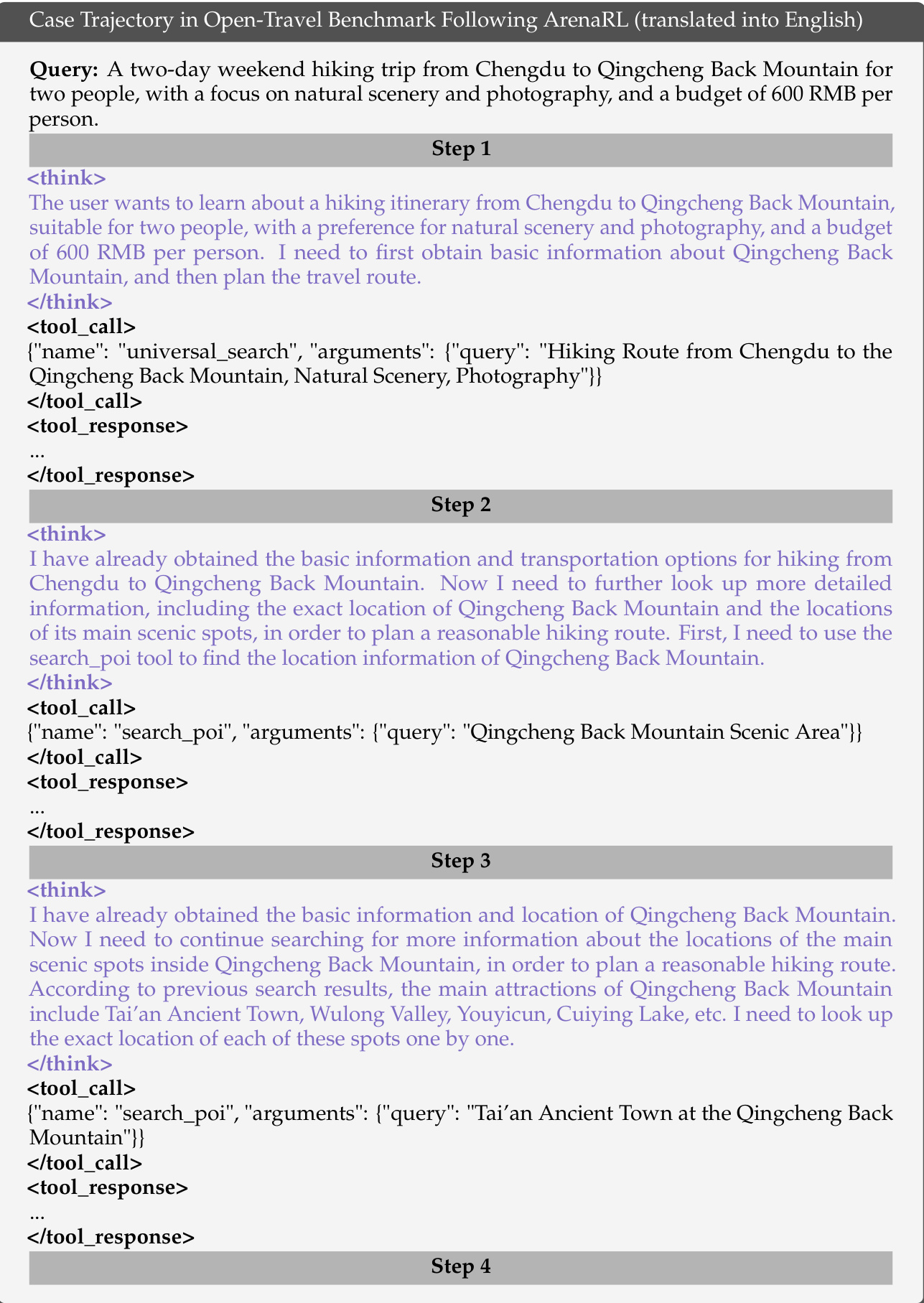
- LLM evaluation consistency with human judgments reaches 73.9%, indicating reliable and human-aligned performance gains. Case studies show ArenaRL generates coherent, constraint-aware, and personalized travel plans, unlike baseline models that produce generic or misaligned outputs.
The authors use ArenaRL to evaluate its performance against closed-source models and reinforcement learning baselines on the Open-Travel and Open-DeepResearch benchmarks. Results show that ArenaRL achieves the highest average win rate of 41.8% on Open-Travel and a win rate of 64.3% with a 99% valid generation rate on Open-DeepResearch, outperforming all other methods in both metrics.
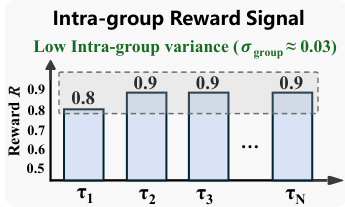
The authors use a tournament-based framework to evaluate the stability of intra-group reward signals, showing that the reward variance across different groups remains consistently low (σ_group ≈ 0.03). Results indicate that the reward values stabilize at approximately 0.9 after the initial group, suggesting that the ranking mechanism produces reliable and consistent feedback for policy optimization.
The authors use the Open-Travel and Open-DeepResearch datasets to evaluate ArenaRL, with training sets comprising SFT and RL data and test sets of 250 and 100 samples respectively. The datasets are designed for multilingual evaluation in travel planning and general open-ended research, with Open-DeepResearch supporting both Chinese and English.
The authors use a tournament-based evaluation framework to compare five different tournament topologies on the Open-Travel benchmark, measuring performance through win rates across subtasks and overall mean. Results show that the Seeded Single-Elimination scheme achieves the highest mean win rate of 32.5%, outperforming other formats and approaching the performance of the computationally expensive Round-Robin tournament while requiring significantly fewer pairwise comparisons.
The authors use ArenaRL to evaluate its performance on open-ended writing tasks across three public benchmarks. Results show that ArenaRL achieves the highest mean score of 80.30, outperforming all closed-source models and fine-tuning baselines, with notable improvements in most subtasks, particularly in the HelloBench-Heur and LongBench-Quality categories.