Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Baichuan-M3: Modeling Clinical Inquiry for Reliable Medical Decision-Making
Baichuan-M3: Modeling Clinical Inquiry for Reliable Medical Decision-Making
Abstract
We introduce Baichuan-M3, a medical-enhanced large language model engineered to shift the paradigm from passive question-answering to active, clinical-grade decision support. Addressing the limitations of existing systems in open-ended consultations, Baichuan-M3 utilizes a specialized training pipeline to model the systematic workflow of a physician. Key capabilities include: (i) proactive information acquisition to resolve ambiguity; (ii) long-horizon reasoning that unifies scattered evidence into coherent diagnoses; and (iii) adaptive hallucination suppression to ensure factual reliability. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that Baichuan-M3 achieves state-of-the-art results on HealthBench, the newly introduced HealthBench-Hallu and ScanBench, significantly outperforming GPT-5.2 in clinical inquiry, advisory and safety. The models are publicly available at https://huggingface.co/collections/baichuan-inc/baichuan-m3.
One-sentence Summary
Baichuan-M3 Team introduces Baichuan-M3, a medical LLM that actively supports clinical decisions via proactive inquiry, long-horizon reasoning, and hallucination suppression, outperforming GPT-5.2 on HealthBench and ScanBench, and is publicly available for real-world healthcare applications.
Key Contributions
- Baichuan-M3 redefines medical LLMs by modeling physician workflows to actively acquire missing information, perform long-horizon reasoning, and suppress hallucinations—addressing the failure of existing systems to stay evidence-grounded during open-ended clinical consultations.
- The model introduces a three-stage training framework with Segmented Pipeline RL and dynamic rubric evolution, aligning optimization with clinical stages (inquiry, testing, diagnosis) to decouple and then integrate competencies for safer, more systematic decision-making.
- Baichuan-M3 achieves state-of-the-art results on HealthBench-Hard (44.4), ScanBench (Clinical Inquiry 74.9, Lab Testing 72.1, Diagnosis 74.4), and hallucination benchmarks, significantly outperforming GPT-5.2 and expert baselines in clinical accuracy and safety.
Introduction
The authors leverage medical LLMs to move beyond passive Q&A toward active, clinical-grade decision support by modeling physician workflows end to end. Prior systems struggle with hallucinations and fragmented reasoning in open-ended consultations, often treating conversational fluency and diagnostic rigor as separate goals—leading to “inquiry inertia” or superficial responses. Baichuan-M3 addresses this by unifying proactive information gathering, long-horizon reasoning, and adaptive hallucination suppression through a three-stage training pipeline that includes Segmented Pipeline RL and dynamic rubric evolution. It achieves state-of-the-art results on HealthBench, HealthBench-Hallu, and ScanBench, outperforming GPT-5.2 in both factual reliability and clinical process fidelity.
Dataset

- The authors use ScanBench, an open-source dataset designed to simulate real clinical workflows through a three-stage sequence: Inquiry → Lab Testing → Diagnosis.
- The dataset includes 303 clinical cases across 12 departments, spanning common specialties (e.g., General Practice) and long-tail ones (e.g., Rheumatology, Hematology).
- Each case is annotated with an average of 29.23 checklist items (range: 20–35), totaling 8,857 items. These reflect clinical diagnostic logic: 55.8% focus on History of Present Illness, 19.6% on Past Medical History, 14.6% on Personal/Social History, and smaller portions on Obstetric/Gynecological (5.4%) and Family History (4.7%).
- Checklist items are weighted for criticality: 51.3% are Level 2 (Critical for diagnosis or risk exclusion), and 48.7% are Level 1 (Supplementary).
- During the examination phase, the model selects from 38 distinct test categories grouped into Routine & Biochemical, Imaging & Functional, and Pathology & Specialized tests — mirroring real-world resource constraints and requiring precise test selection to avoid waste.
Method
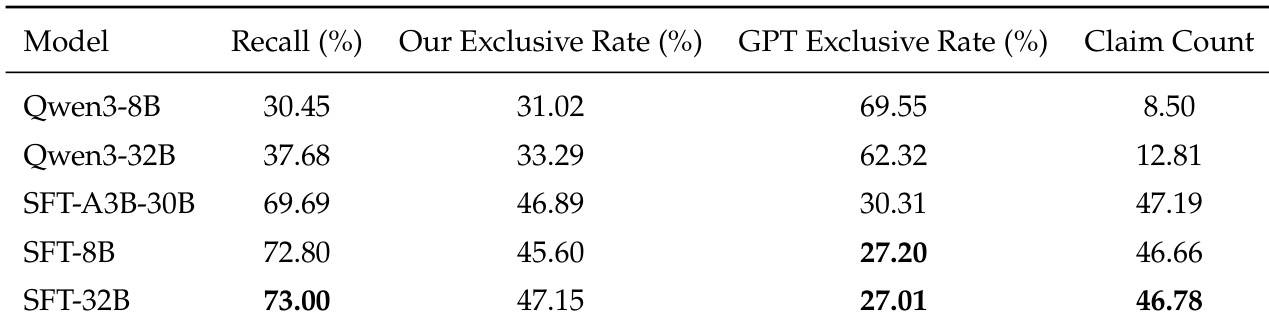
The authors leverage a multi-stage, task-specialized training infrastructure to develop Baichuan-M3, a medical large language model optimized for long-horizon diagnostic reasoning and credible advisory generation. The core architecture is built around three progressive training stages—Capability Learning, Distribution Fusion, and Policy Unification—each designed to isolate and resolve distinct optimization challenges inherent in multi-task medical reasoning.
Refer to the framework diagram, which illustrates the overall training pipeline. In Stage 1, the authors deploy independent reinforcement learning (RL) pipelines for distinct capability domains—Clinical Inquiry, Healthcare Consultation, and General Reasoning—starting from a shared initialization. Each domain-specific expert is optimized under its own task-specific reward signal, allowing for the emergence of strong, differentiated inductive biases without gradient interference. This stage produces a set of specialized teacher models, each excelling in its designated domain.
Stage 2 transitions to offline policy distillation. The authors freeze the teacher models and generate rollouts to construct an offline trajectory dataset. The student model learns from this data using a Clip-Forward-KL objective, which enforces a one-sided constraint: updates are only applied when the student’s token probability is lower than the teacher’s. This prevents overfitting to sparse samples and preserves entropy outside the data support, enabling the student to broadly cover high-probability regions of multiple expert distributions. The design mitigates mode collapse and provides a stable initialization for the final stage.
In Stage 3, the student model re-enters the online environment and performs rollouts across mixed domain distributions. Here, the model is simultaneously constrained by ground-truth task rewards and multi-teacher priors. The authors employ reverse KL regularization, which drives the student to select the optimal mode when faced with conflicting advice, rather than averaging them. This transforms the student from an imitator into a decision-maker, achieving deep policy unification. The framework supports iterative refinement: the unified model can be re-initialized as a new teacher for Stage 1, enabling continuous capability enhancement.
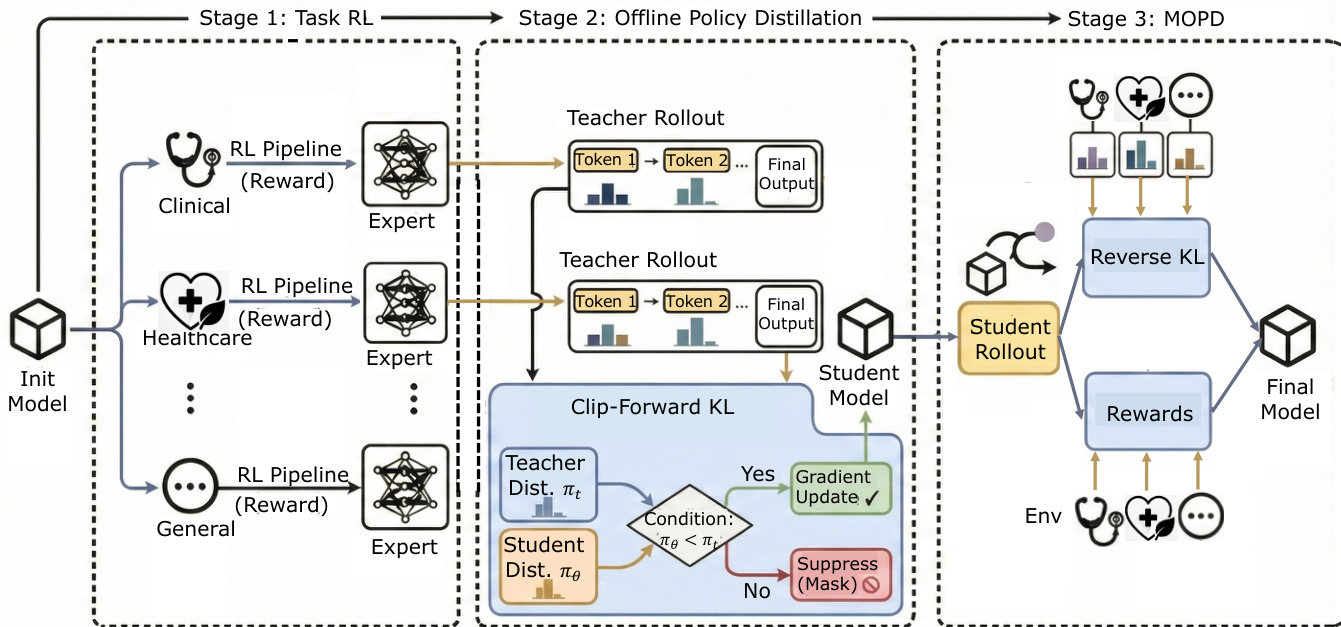
For task-specific optimization, the authors implement a segmented pipeline for clinical consultation, dividing the diagnostic process into four stages: Inquiry, Differential Diagnosis (DDX), Lab Testing, and Final Diagnosis. As shown in the figure below, the training system schedules multiple task slots in parallel, each operating on a different stage or patient case. The policy generates a response segment for the current stage, which is then appended to the context for the next stage. A Quality-Gated Transition mechanism filters trajectories based on a stage-specific verifier score, ensuring only clinically valid chains are extended.
To address credit assignment in long-horizon dialogues, the authors introduce SPAR (Step-Penalized Advantage with Relative baseline). SPAR computes a step-wise advantage by comparing the penalized return of each interaction step against an unpenalized group average. This decouples local penalties from the global baseline, enabling precise attribution of rewards and penalties to specific steps. The advantage formulation induces an implicit curriculum: early training prioritizes correcting critical errors (e.g., redundancy), while later phases refine stylistic nuances as global reward variance decreases.
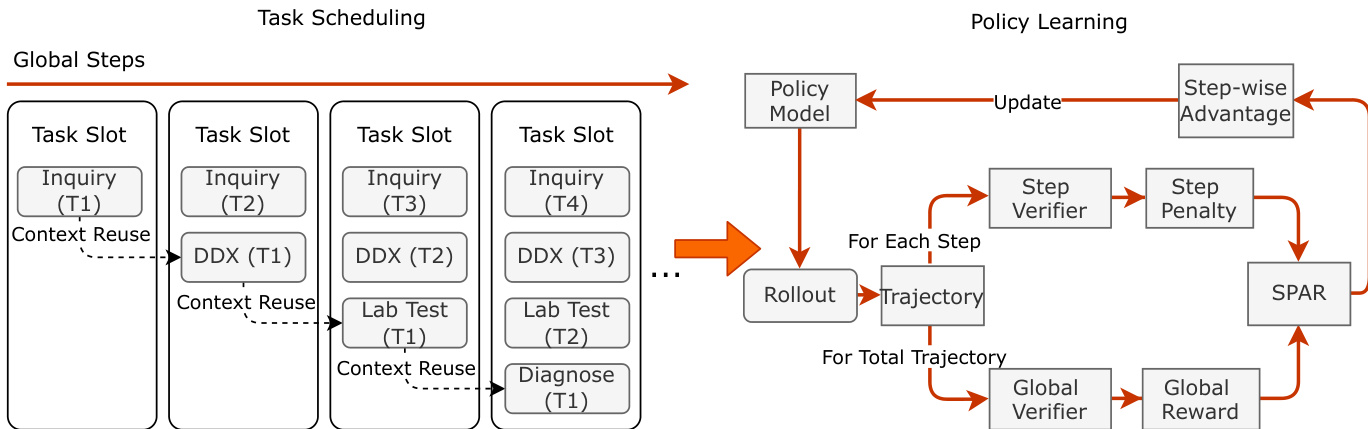
For credible healthcare advisory, the authors implement a Fact-Aware Reinforcement Learning framework. As depicted in the figure, the system decomposes the model’s response into atomic claims, which are then weighted by semantic saliency and verified against authoritative sources via a multi-turn search agent. A two-level caching system—exact match and semantic match—reduces external search requests by 85%, making real-time verification feasible in the RL loop. The final reward aggregates task utility with a dynamically gated hallucination penalty, where the penalty intensity is modulated by the model’s task reward performance. This ensures that factual constraints are only enforced once the model demonstrates sufficient reasoning competence.
For inference optimization, the authors integrate Gated Eagle-3 speculative decoding. The draft model is augmented with a Gated-Attention module that dynamically regulates information flow from the target model’s hidden states, preventing representation mismatch and improving candidate acceptance rates. As shown in the figure, the gating unit applies element-wise multiplication to modulate attention outputs, emphasizing salient features while suppressing noise. This design yields a 12% throughput improvement over standard Eagle-3.
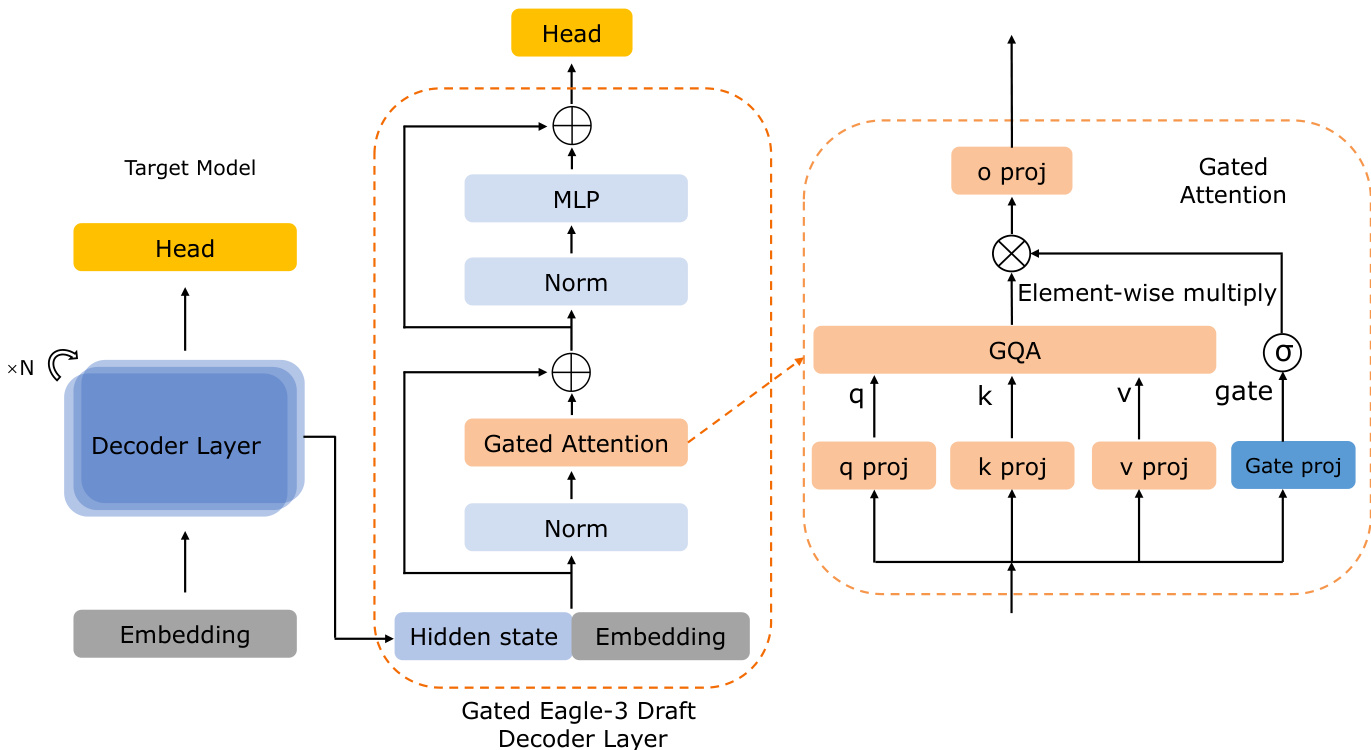
Additionally, the authors apply INT4 quantization using a self-generated calibration scheme to ensure uniform expert coverage in the Mixture-of-Experts architecture. This mitigates calibration bias and preserves near-lossless performance relative to the BF16 model, enabling efficient deployment in resource-constrained settings.
Experiment
- Baichuan-M3 outperforms leading general and medical-specific LLMs, as well as human physicians, across dynamic clinical workflows and broad medical reasoning tasks, demonstrating superior end-to-end diagnostic capability.
- It excels in safety-critical areas like risk stratification and differential diagnosis, significantly surpassing both AI models and human experts in identifying red-flag symptoms and uncovering hidden clinical clues.
- The model improves with dialogue length, showing sustained reasoning growth while generalist models plateau, highlighting its capacity for context-aware, iterative clinical inquiry.
- Baichuan-M3 sets a new state-of-the-art on HealthBench, particularly in challenging cases, while maintaining the lowest hallucination rate, reflecting a strong balance between depth of reasoning and factual reliability.
- Fact-Aware RL reduces hallucinations by aligning outputs with internal knowledge, minimizing unfaithful errors without sacrificing reasoning power, effectively decoupling safety from capability degradation.
- SPAR enables efficient, non-redundant multi-turn consultations by providing step-level rewards, preserving logical coherence while maximizing information extraction per turn.
- Ablation studies confirm that Clip-Forward-KL enables better fusion of medical expertise without compromising existing inquiry skills, and Gated Eagle-3 enhances inference efficiency without compromising accuracy.
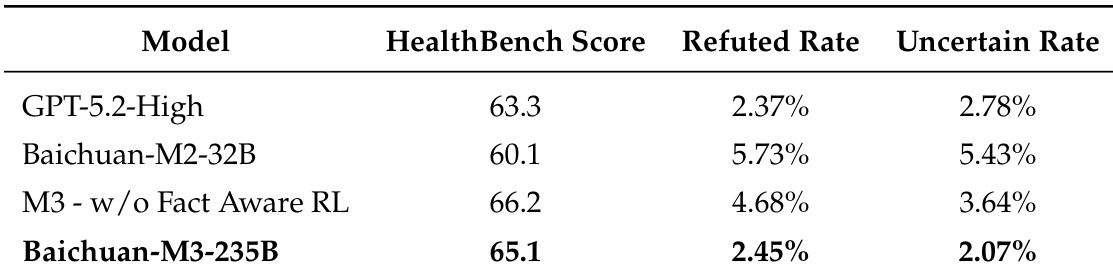
The authors use Fact-Aware Reinforcement Learning to refine Baichuan-M3, achieving a significant reduction in both refuted and uncertain hallucination rates while maintaining competitive task performance. Results show that the model balances factual accuracy with clinical reasoning capability more effectively than its predecessor and leading general-purpose LLMs. This indicates that targeted safety training can mitigate hallucinations without degrading the model’s utility in complex medical tasks.
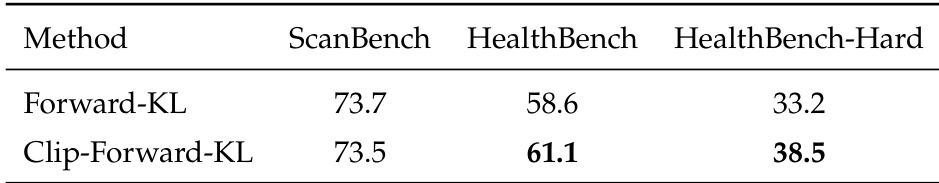
The authors use Clip-Forward-KL to improve the fusion of healthcare expertise during offline distillation, achieving higher scores on HealthBench and HealthBench-Hard while maintaining performance on ScanBench. Results show that Clip-Forward-KL mitigates the over-amplification of sparse samples seen with standard Forward-KL, enabling more conservative and effective integration of new domain knowledge. This approach preserves existing inquiry capabilities while enhancing broader medical reasoning performance.
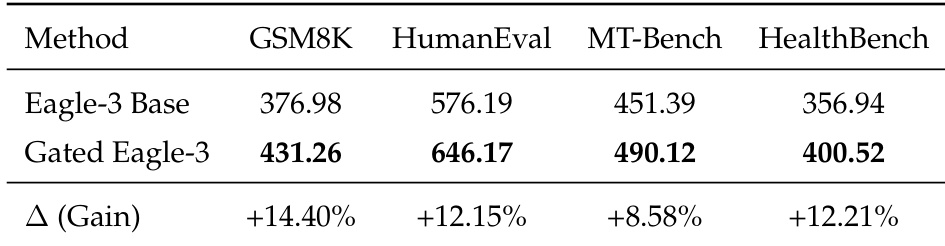
The authors use Gated Eagle-3 to enhance speculative decoding performance, achieving consistent gains across multiple benchmarks including GSM8K, HumanEval, MT-Bench, and HealthBench. Results show measurable improvements in average acceptance length and throughput compared to the base Eagle-3 model, indicating more efficient inference without compromising output quality. This optimization supports faster and more reliable deployment in both general and medical reasoning tasks.
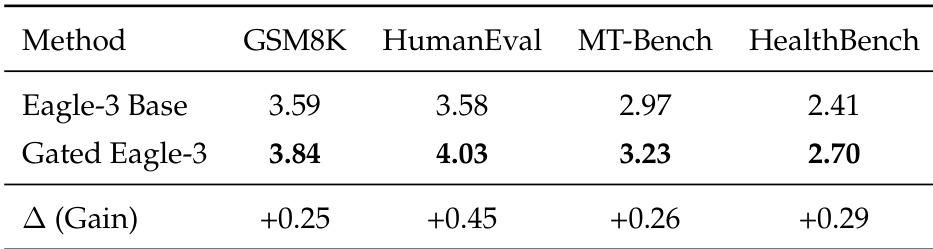
The authors use Gated Eagle-3 to enhance speculative decoding, achieving consistent performance gains across multiple benchmarks including GSM8K, HumanEval, MT-Bench, and HealthBench. Results show that Gated Eagle-3 improves average acceptance length and throughput compared to the base Eagle-3 model, indicating more efficient inference without compromising task accuracy. This optimization proves effective in both general reasoning and specialized medical evaluation settings.
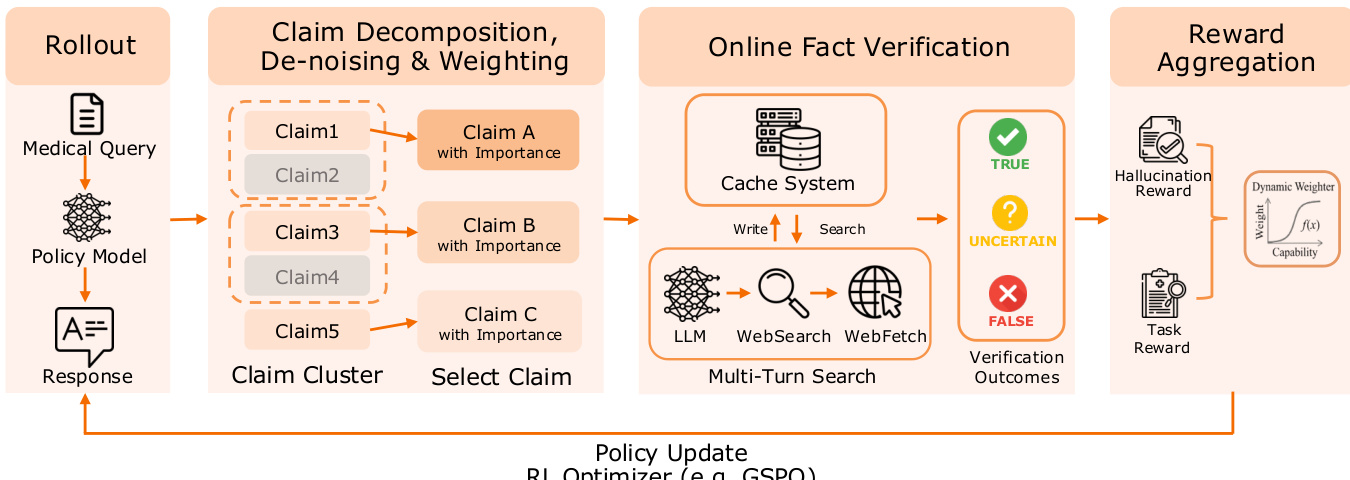
The authors use supervised fine-tuning to adapt smaller models for efficient claim extraction during online reinforcement learning, finding that an 8B model achieves 72.80% recall relative to GPT-5 while balancing fidelity and deployment cost. Results show that larger models offer only marginal gains in recall, with the 32B variant providing no significant advantage over the 8B model despite higher computational demands. The SFT-8B model is selected as the optimal extractor, maintaining high coverage while minimizing exclusive claims not captured by the reference baseline.