Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Modality Gap-Driven Subspace Alignment Training Paradigm For Multimodal Large Language Models
Modality Gap-Driven Subspace Alignment Training Paradigm For Multimodal Large Language Models
Abstract
Despite the success of multimodal contrastive learning in aligning visual and linguistic representations, a persistent geometric anomaly, the Modality Gap, remains: embeddings of distinct modalities expressing identical semantics occupy systematically offset regions. Prior approaches to bridge this gap are largely limited by oversimplified isotropic assumptions, hindering their application in large-scale scenarios. In this paper, we address these limitations by precisely characterizing the geometric shape of the modality gap and leveraging it for efficient model scaling. First, we propose the Fixed-frame Modality Gap Theory, which decomposes the modality gap within a frozen reference frame into stable biases and anisotropic residuals. Guided by this precise modeling, we introduce ReAlign, a training-free modality alignment strategy. Utilizing statistics from massive unpaired data, ReAlign aligns text representation into the image representation distribution via a three-step process comprising Anchor, Trace, and Centroid Alignment, thereby explicitly rectifying geometric misalignment. Building on ReAlign, we propose ReVision, a scalable training paradigm for Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). ReVision integrates ReAlign into the pretraining stage, enabling the model to learn the distribution of visual representations from unpaired text before visual instruction tuning, without the need for large-scale, high-quality image-text pairs. Our framework demonstrates that statistically aligned unpaired data can effectively substitute for expensive image-text pairs, offering a robust path for the efficient scaling of MLLMs.
One-sentence Summary
Researchers from HKUST(GZ), NUS, and collaborators propose ReAlign and ReVision to resolve the modality gap in multimodal learning by modeling its geometric structure—stable bias and anisotropic residuals—enabling efficient, training-free alignment and scalable MLLM pretraining using unpaired data instead of costly image-text pairs.
Key Contributions
- We introduce the Fixed-frame Modality Gap Theory, which decomposes the geometric misalignment between visual and text embeddings into stable biases and anisotropic residuals within a frozen reference frame, correcting prior oversimplified isotropic assumptions.
- We propose ReAlign, a training-free alignment method that uses statistics from unpaired data to map text representations into the image embedding space via Anchor, Trace, and Centroid Alignment, enabling precise geometric correction without additional training.
- We present ReVision, a scalable MLLM pretraining paradigm that leverages ReAlign to substitute expensive image-text pairs with unpaired text data, allowing models to learn visual distributions before instruction tuning while maintaining performance.
Introduction
The authors leverage multimodal contrastive learning’s known geometric flaw—the Modality Gap—to rethink how Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) are trained. Prior methods assume this gap is isotropic noise and correct only the mean shift, which fails to capture the true anisotropic structure of representation misalignment and limits scalability. The authors’ key contribution is a precise geometric decomposition of the gap into stable biases and anisotropic residuals, enabling ReAlign: a training-free, three-step statistical alignment that maps text embeddings into the visual distribution using only unpaired data. Building on this, they introduce ReVision, a scalable two-stage training paradigm that substitutes expensive image-text pairs with massive text during pretraining, then refines with real images—proving text alone can encode rich visual semantics when aligned correctly.
Method
The authors leverage a fixed-reference framework to decompose the modality gap into interpretable geometric components, enabling precise characterization of persistent misalignments in dual-encoder contrastive models. This decomposition is grounded in a data-driven subspace construction that separates bias and residual terms, allowing independent estimation and reducing theoretical claims to second-moment conditions estimable from finite samples.
The framework begins by training a dual-encoder model using the InfoNCE loss on a large-scale image-text dataset. At a fixed reference time t0, a task-relevant subspace U is constructed from a held-out probe set by computing the empirical covariance of unit-normalized embeddings for both modalities:
Σ^(t0):=Covp(ex(t0))+Covp(ey(t0)),where U:=span{q1,…,qr} is derived from the top r eigenvectors of Σ^(t0), determined by an energy threshold. The orthogonal complement V:=U⊥ is then defined, and fixed orthogonal projectors PU and PV are maintained for all subsequent analysis. This fixed frame enables consistent decomposition of the modality gap Δ(t):=ex(t)−ey(t) into bias and residual components.
The bias terms are defined as projected mean components: β(t):=PUE[Δ(t)]∈U (Principal Modality Bias, PMB) and γ(t):=PVE[Δ(t)]∈V (Constant Orthogonal Bias, COB). The zero-mean residuals are δ(t):=PU(Δ(t)−E[Δ(t)])∈U and ζ(t):=PV(Δ(t)−E[Δ(t)])∈V. This yields the exact orthogonal decomposition:
Δ(t)=β(t)+δ(t)+γ(t)+ζ(t).As shown in the figure below, the residual structure exhibits extreme anisotropy in both subspaces, with the orthogonal component V hosting a stable bias vector that remains geometrically decoupled from the highly stretched noise structure of ζ(t).
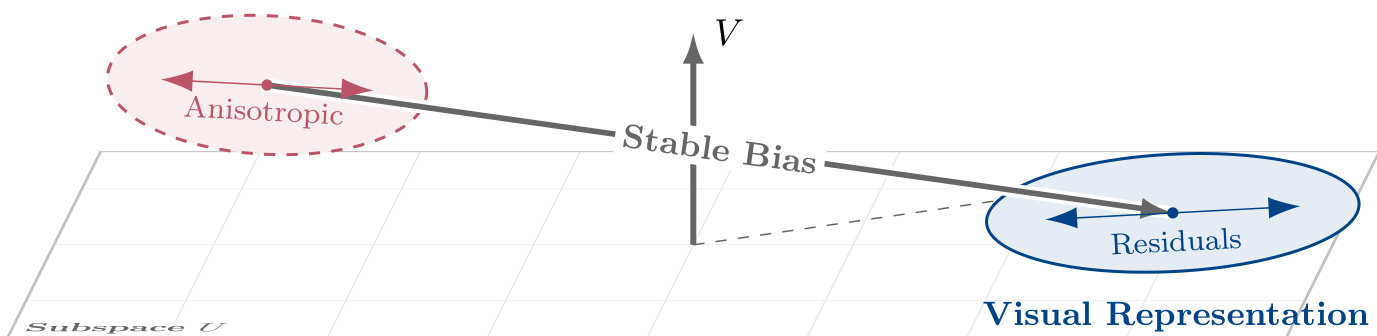
The authors further analyze the evolution of these components. Gradients are empirically observed to concentrate within the instantaneous task subspace Ut, with the reference leakage ratio ∥PVgt∥/∥gt∥ tightly tracking the geometric baseline sinθ(Ut,U). This concentration implies that direct optimization in V is negligible, leading to passive drift of γ(t) — a slow, cumulative evolution driven by subspace rotation rather than active gradient correction. In contrast, within U, the residual δ(t) exhibits extreme anisotropy (κ(ΣU)>103) and rapidly aligns with the gradient covariance structure, indicating that fluctuations are semantically coupled to the task.
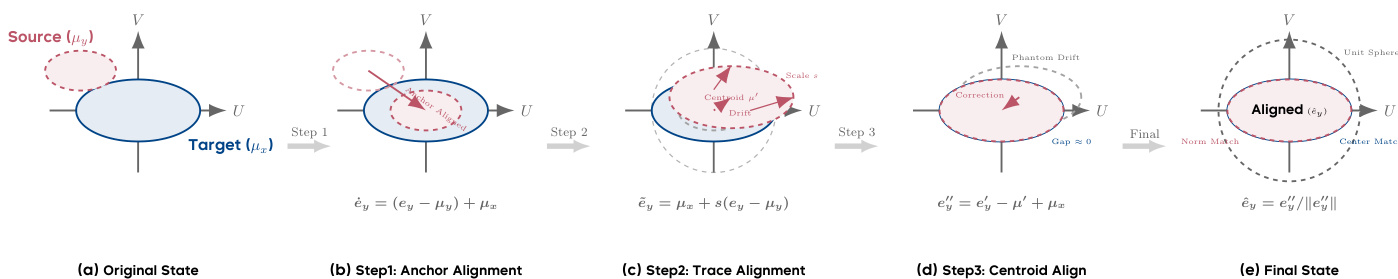
To address these geometric misalignments without retraining, the authors propose ReAlign, a three-stage, training-free alignment strategy. The method operates in Euclidean space before spherical projection and consists of:
- Anchor Alignment: Centering the source modality and shifting its mean to match the target’s centroid: e˙y=(ey−μy)+μx.
- Trace Alignment: Scaling the residuals to match the target’s global energy via s=Tx/Ty, yielding e~y=μx+s(ey−μy), preserving the source’s anisotropic structure.
- Centroid Alignment: Correcting the non-linear drift induced by spherical projection by explicitly re-centering the distribution: ey′′=ey′−μ′+μx, followed by re-normalization.
As illustrated in the ReAlign pipeline, this sequence ensures that the final aligned representation matches both the first- and second-order statistics of the target modality on the unit hypersphere, while preserving semantic hierarchy and mitigating phantom drift.
This geometrically grounded approach forms the foundation for ReVision, a scalable two-stage training paradigm for multimodal LLMs. In Stage 1, ReAlign is used to synthesize pseudo-visual embeddings from unpaired text, enabling pretraining on vast textual corpora. In Stage 2, the model is fine-tuned on real image-instruction pairs to refine fine-grained visual reasoning. During inference, the model directly consumes real images, benefiting from the asymmetric alignment established during pretraining.
Experiment
- ReAlign effectively reduces modality gap by modeling anisotropic covariance, outperforming isotropic methods like C³ that hit geometric bottlenecks.
- ReVision achieves superior performance in multimodal LLM training by preserving semantic hierarchy and angular topology, leading to better reasoning and reduced hallucinations.
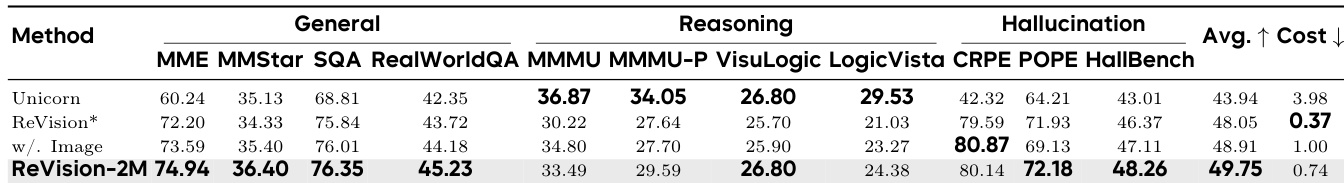
- Scaling unpaired text data (2M samples) with ReAlign surpasses performance of 1M real image-text pairs at 26% lower cost, proving cost-efficient scaling is viable.
- ReAlign demonstrates rapid convergence with ~10K samples, stable numerical precision in Float64, linear time complexity, and constant memory usage, enabling scalable deployment.
- Domain-specific statistics are essential; cross-domain alignment degrades performance, highlighting the need for tailored calibration.
- Blockwise covariance alignment fails due to numerical instability and semantic distortion, while ReAlign’s isotropic scaling preserves local structure and ensures robustness.
- Short captions outperform long ones due to compact, low-rank covariance and higher signal-to-noise ratio, revealing that linguistic density can harm geometric alignment.
- Qualitative analysis confirms ReVision excels in abstract reasoning, spatial understanding, fine-grained perception, and knowledge integration across diverse cognitive tasks.
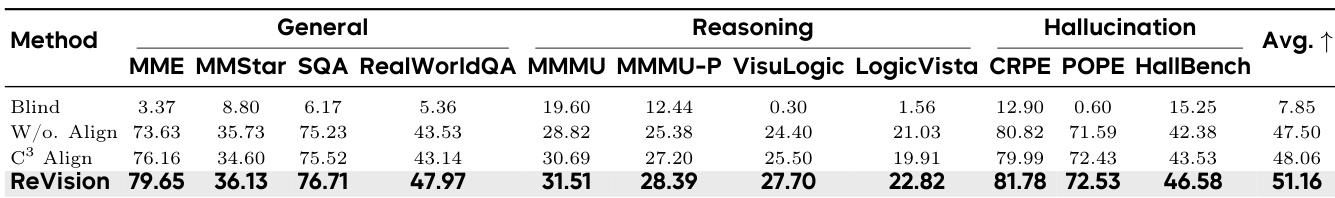
ReVision outperforms BC Align across all evaluated categories, including general perception, complex reasoning, and hallucination resistance, achieving a higher average score. The results confirm that ReVision’s geometric alignment strategy preserves semantic structure better than blockwise covariance methods, which suffer from numerical instability and semantic distortion. This leads to more robust and accurate multimodal understanding without requiring paired image-text data.
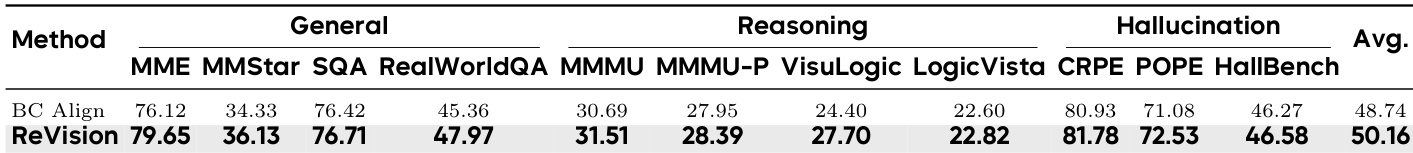
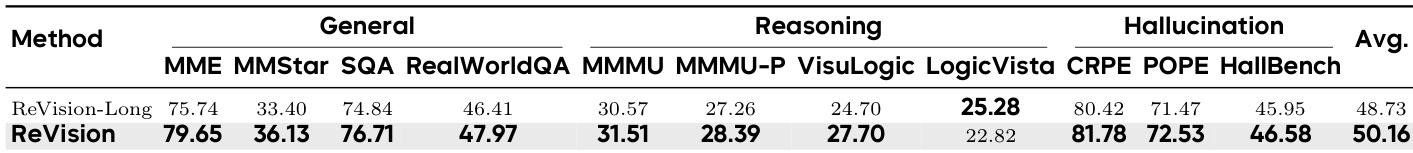
Results show that ReVision, which uses anisotropic geometric alignment, consistently outperforms its long-caption variant across general perception, reasoning, and hallucination benchmarks. The performance gap highlights that concise, geometrically compact captions enable more stable modality alignment than linguistically rich but noisy long captions. This suggests that signal-to-noise ratio and manifold structure matter more than raw textual length for effective cross-modal training.
The authors use ReVision to align text and image modalities by modeling anisotropic covariance, which significantly reduces the geometric gap compared to isotropic methods like C³. Results show that ReVision outperforms baselines across general perception, reasoning, and hallucination benchmarks, demonstrating that precise geometric alignment preserves semantic structure and improves downstream task performance. Scaling up text-only pretraining with ReVision also surpasses paired image-text training in performance while reducing data acquisition costs.
ReVision-2M achieves the highest average score across general, reasoning, and hallucination benchmarks, outperforming both text-only and paired image-text baselines while reducing data acquisition cost by 26%. The method’s geometric alignment strategy preserves semantic structure better than isotropic noise-based approaches, enabling superior performance even without real image inputs. Scaling up unpaired text data with precise alignment proves more cost-effective and competitive than relying on expensive paired datasets.