Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
BitDance: Scaling Autoregressive Generative Models with Binary Tokens
BitDance: Scaling Autoregressive Generative Models with Binary Tokens
Yuang Ai Jiaming Han Shaobin Zhuang Weijia Mao Xuefeng Hu Ziyan Yang Zhenheng Yang Huaibo Huang Xiangyu Yue Hao Chen
Abstract
We present BitDance, a scalable autoregressive (AR) image generator that predicts binary visual tokens instead of codebook indices. With high-entropy binary latents, BitDance lets each token represent up to 2^{256} states, yielding a compact yet highly expressive discrete representation. Sampling from such a huge token space is difficult with standard classification. To resolve this, BitDance uses a binary diffusion head: instead of predicting an index with softmax, it employs continuous-space diffusion to generate the binary tokens. Furthermore, we propose next-patch diffusion, a new decoding method that predicts multiple tokens in parallel with high accuracy, greatly speeding up inference. On ImageNet 256x256, BitDance achieves an FID of 1.24, the best among AR models. With next-patch diffusion, BitDance beats state-of-the-art parallel AR models that use 1.4B parameters, while using 5.4x fewer parameters (260M) and achieving 8.7x speedup. For text-to-image generation, BitDance trains on large-scale multimodal tokens and generates high-resolution, photorealistic images efficiently, showing strong performance and favorable scaling. When generating 1024x1024 images, BitDance achieves a speedup of over 30x compared to prior AR models. We release code and models to facilitate further research on AR foundation models. Code and models are available at: https://github.com/shallowdream204/BitDance.
One-sentence Summary
Researchers from ByteDance, CUHK, and CAS propose BitDance, an AR image generator using binary tokens and diffusion heads for efficient sampling, achieving state-of-the-art FID with 5.4× fewer parameters and 8.7× speedup, excelling in high-resolution text-to-image generation.
Key Contributions
- BitDance introduces a scalable autoregressive image generator that predicts binary visual tokens with up to 2256 states per token, enabling high-fidelity reconstruction while avoiding codebook collapse and quantization errors common in discrete VQ-based approaches.
- To efficiently sample from this massive token space, BitDance replaces softmax classification with a binary diffusion head and introduces next-patch diffusion, allowing parallel multi-token prediction that reduces parameter count and accelerates inference by up to 8.7× compared to prior parallel AR models.
- Evaluated on ImageNet 256×256 and text-to-image tasks, BitDance achieves state-of-the-art FID of 1.24 among AR models and generates 1024×1024 images with over 30× speedup, while using 5.4× fewer parameters than competing 1.4B-parameter models.
Introduction
The authors leverage binary visual tokens—instead of discrete codebook indices—to build BitDance, a highly scalable autoregressive image generator that achieves compact, high-entropy representations capable of encoding up to 2^256 states per token. Prior discrete tokenizers suffer from quantization errors and memory-heavy entropy losses, while continuous token approaches in AR models face error accumulation and drift during long-sequence generation. BitDance overcomes these by introducing a binary diffusion head for token generation and next-patch diffusion for parallel multi-token prediction, enabling 8.7x faster inference than prior parallel AR models while using 5.4x fewer parameters and achieving state-of-the-art FID scores. It also scales efficiently to 1024x1024 text-to-image generation with over 30x speedup, making high-fidelity autoregressive generation practical for large-scale applications.
Method
The authors leverage a novel autoregressive architecture called BitDance, designed to scale token entropy for high-fidelity visual generation while maintaining computational efficiency. The core innovation lies in replacing conventional discrete classification heads with a continuous-space diffusion-based prediction mechanism, enabling precise and scalable sampling of binary visual tokens.
The framework begins with a binary visual tokenizer based on Lookup-Free Quantization (LFQ), which maps continuous latent vectors x∈Rd to binary tokens via xq=sign(x). To prevent codebook collapse and maximize entropy, a group-wise entropy loss is applied, partitioning the d channels into g groups for tractable computation. This allows scaling the codebook size up to 2256, achieving reconstruction fidelity comparable to continuous VAEs.
For token prediction, BitDance introduces a binary diffusion head that models the joint distribution of binary tokens in continuous space. Instead of predicting discrete indices, the model treats each d-bit token as a point on a d-dimensional hypercube. Given a hidden state z∈Rh, the diffusion head learns to predict the target token x∈Rd by optimizing a velocity-matching loss:
L(z,x)=Et,x,ϵ∥vθ(xt,t,z)−vt∥2,where xt=tx+(1−t)ϵ and vt=x−ϵ. During inference, the model initializes x0∼N(0,I) and integrates the velocity field using an Euler solver over N steps, followed by a hard binarization x1=sign(x1) to project the output back onto the hypercube vertices. This geometric constraint enhances stability and convergence.
Refer to the framework diagram, which illustrates the architecture of BitDance trained on multi-modal tokens. An input image is encoded into binary latents, flattened into a 1D sequence via patch-wise raster scan, and processed by an autoregressive transformer. The binary diffusion head enables efficient parallel prediction of multiple tokens per step.
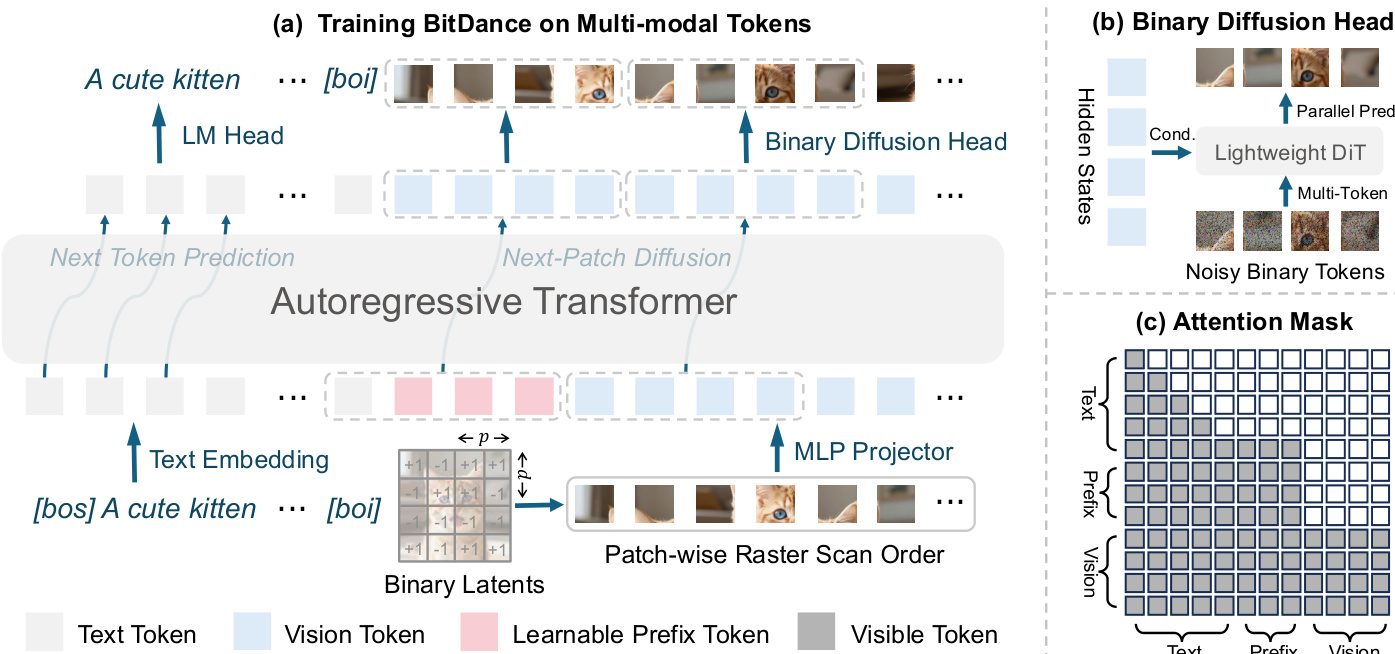
To accelerate generation, BitDance employs a next-patch diffusion paradigm. Rather than predicting tokens one by one, the model partitions the sequence into M patches of p×p tokens and predicts each patch jointly. This is implemented via a block-wise causal attention mask that allows intra-patch tokens to attend to each other while preserving autoregressive dependencies across patches. To support this, p2−1 learnable prefix tokens are prepended to the visual sequence.
The binary diffusion head is extended to support multi-token prediction by adapting the velocity-matching loss to a patch of tokens X∈Rp2×d conditioned on hidden states Z∈Rp2×h:
Lparallel=Et,X,ϵ∥vθ(Xt,t,Z)−vt∥2.The prediction network fθ is implemented as a lightweight DiT to efficiently model the joint distribution of p2 tokens. This design bridges the training-inference gap present in prior parallel AR models, which rely on independent token sampling despite modeling joint distributions.
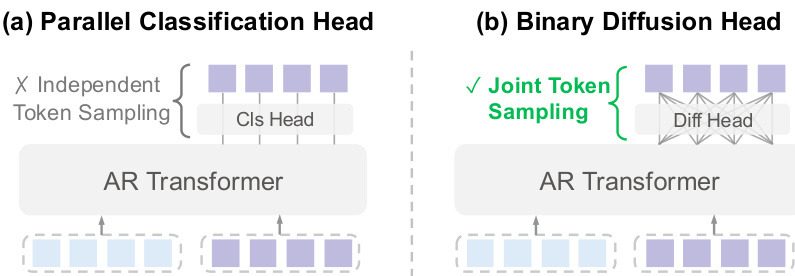
As shown in the figure below, the binary diffusion head enables joint token sampling, in contrast to parallel classification heads that sample tokens independently, violating the required joint distribution.
For text-to-image generation, BitDance is built atop a pretrained LLM (Qwen3-14B), serving as both text encoder and image generator. The model is trained using a three-stage pipeline: pre-training, continued training, and supervised fine-tuning, with mixed-resolution training (256px, 512px, 1024px) to ensure stability and generalization. A distillation stage further increases parallelism from 16 to 64 tokens per step. The training loss combines vision loss from the diffusion head and text loss (cross-entropy) with a 1:0.01 weighting, and classifier-free guidance is enabled via 10% token dropout.
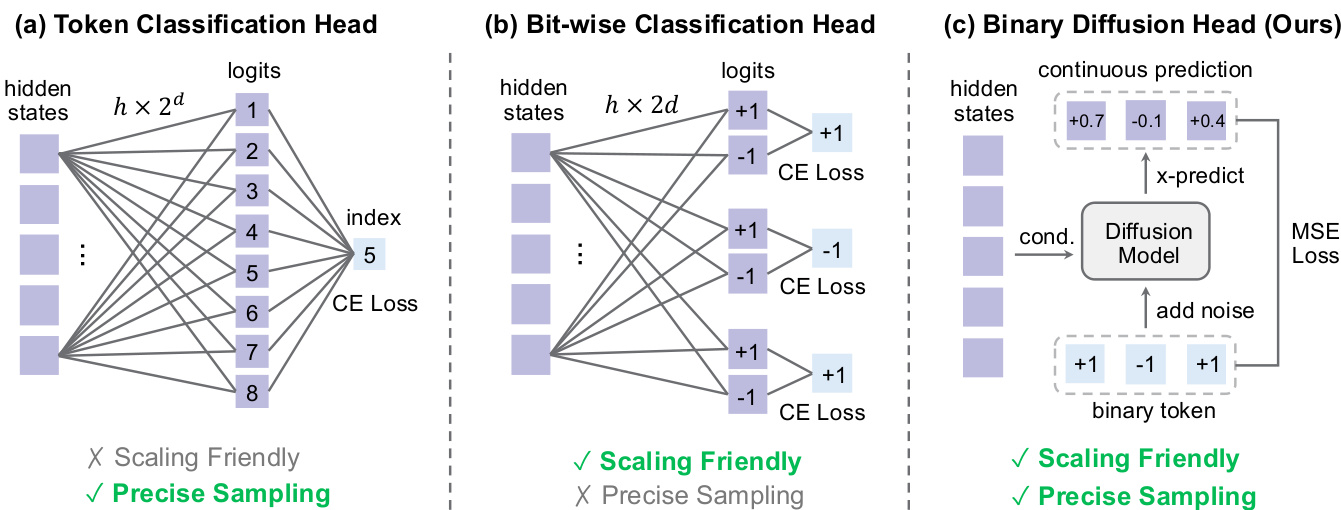
The binary diffusion head’s effectiveness stems from the geometric structure of binary tokens as hypercube vertices. This finite, orientation-constrained space provides strong regularization, reducing optimization complexity and improving sampling stability compared to unconstrained continuous latent spaces. As illustrated in the comparison of binary token sampling paradigms, the diffusion head achieves both scaling efficiency and precise sampling, overcoming the limitations of index-based and bit-wise classification approaches.
Experiment
- Scaling token entropy improves discrete tokenizer reconstruction, matching or exceeding continuous models, especially with larger codebooks and downsampling ratios.
- Larger autoregressive Transformers better exploit increased vocabulary sizes, showing that model scale must grow alongside token entropy for optimal generative performance.
- BitDance achieves state-of-the-art or near-state-of-the-art results on ImageNet and text-to-image benchmarks, outperforming larger parallel AR models while using fewer parameters and less training data.
- The binary diffusion head enables efficient parallel token generation, maintains high quality with few sampling steps, and implicitly learns discrete distributions without explicit constraints.
- Ablations confirm the superiority of binary tokenization over continuous VAEs, the effectiveness of patch-wise raster scan and block causal masks, and the limitations of alternative sampling heads.
- BitDance demonstrates strong data efficiency, matching proprietary models despite training on orders of magnitude less data, and excels in prompt following, text fidelity, and inference speed.
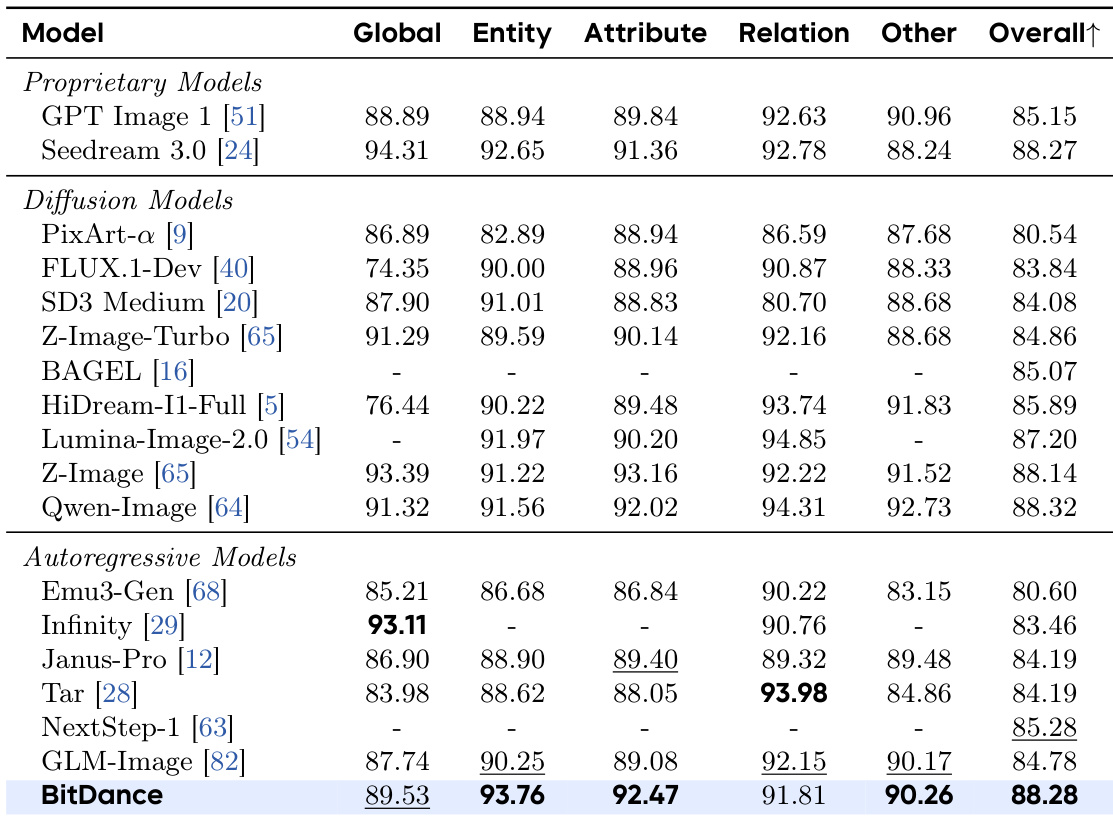
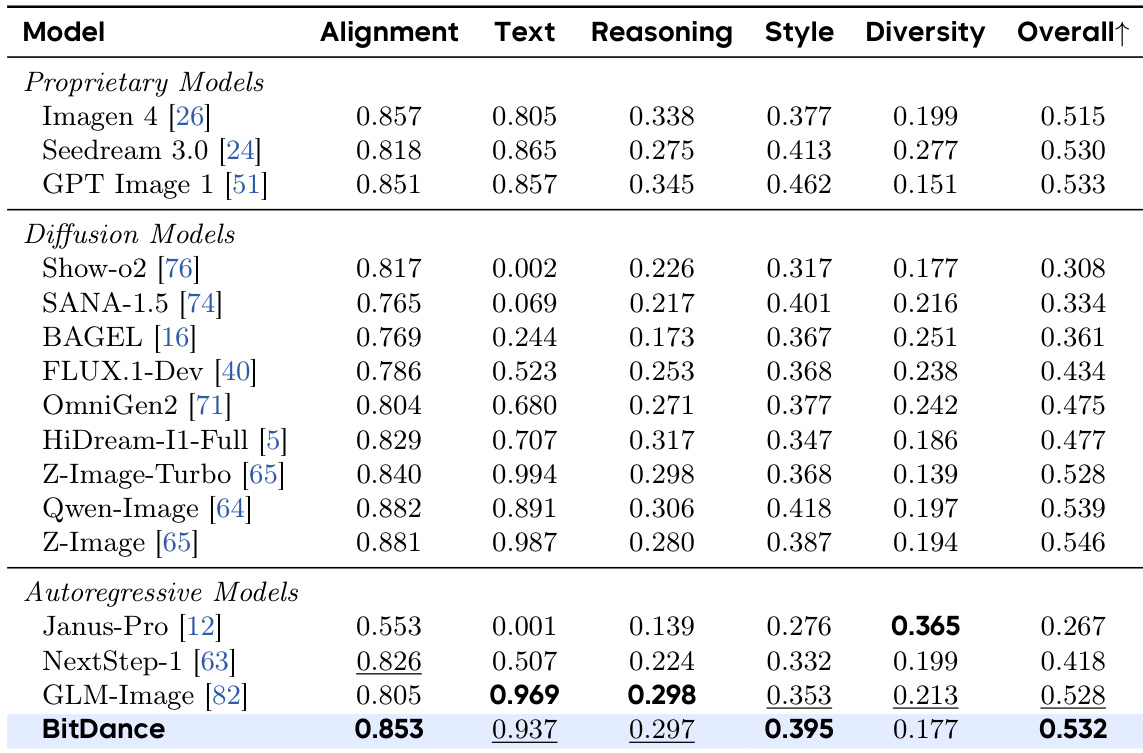
Results show that BitDance achieves state-of-the-art performance among autoregressive models on text-to-image generation benchmarks, matching or exceeding many proprietary and diffusion-based systems despite being trained on significantly less data. The model demonstrates strong capabilities in prompt following, text rendering, and reasoning across multiple evaluation dimensions. Its efficiency and scalability allow it to close the performance gap between open-source and commercial models while maintaining faster inference speeds.
The authors evaluate different sampling heads for autoregressive image generation and find that the binary diffusion head significantly outperforms alternatives in both FID and Inception Score. While token classification fails due to memory constraints and bitwise classification underperforms from oversimplified assumptions, the binary diffusion head achieves superior quality by effectively modeling discrete token distributions. Results confirm that this design enables robust, high-fidelity generation with minimal sampling steps.

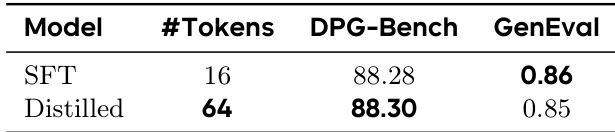
The authors evaluate two variants of their text-to-image model—SFT and Distilled—on benchmark metrics, showing that the Distilled version, which generates 64 tokens in parallel, achieves a slightly higher DPG-Bench score while maintaining comparable GenEval performance. This indicates that distillation preserves generation quality while enabling faster inference through increased parallelism.
Results show that BitDance achieves state-of-the-art performance among autoregressive models on text-to-image generation benchmarks, matching or exceeding leading proprietary and diffusion models in key capabilities like prompt alignment and text rendering. The model attains these results despite being trained on significantly less data, highlighting its efficiency and strong generalization. Its performance across multiple evaluation dimensions underscores the effectiveness of its architecture in bridging the gap between open-source and commercial systems.
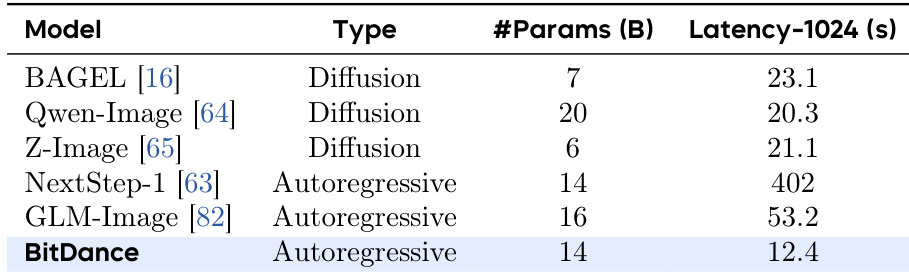
The authors evaluate BitDance against other image generation models and find it achieves significantly lower latency despite matching the parameter scale of larger autoregressive models. Results show BitDance generates 1024×1024 images faster than both diffusion and autoregressive baselines, highlighting its efficiency in inference speed. This performance is achieved without compromising generative quality, as demonstrated in prior benchmarks.